This project showcases the implementation of a computation server capable of handling both synchronous and asynchronous Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs). The server supports two basic operations: addition of two numbers and sorting an array. In synchronous mode, the client waits for the server to complete the computation before proceeding, while in asynchronous mode, the client continues with other tasks after receiving an acknowledgment from the server. The server returns the result to the client once the computation is complete.
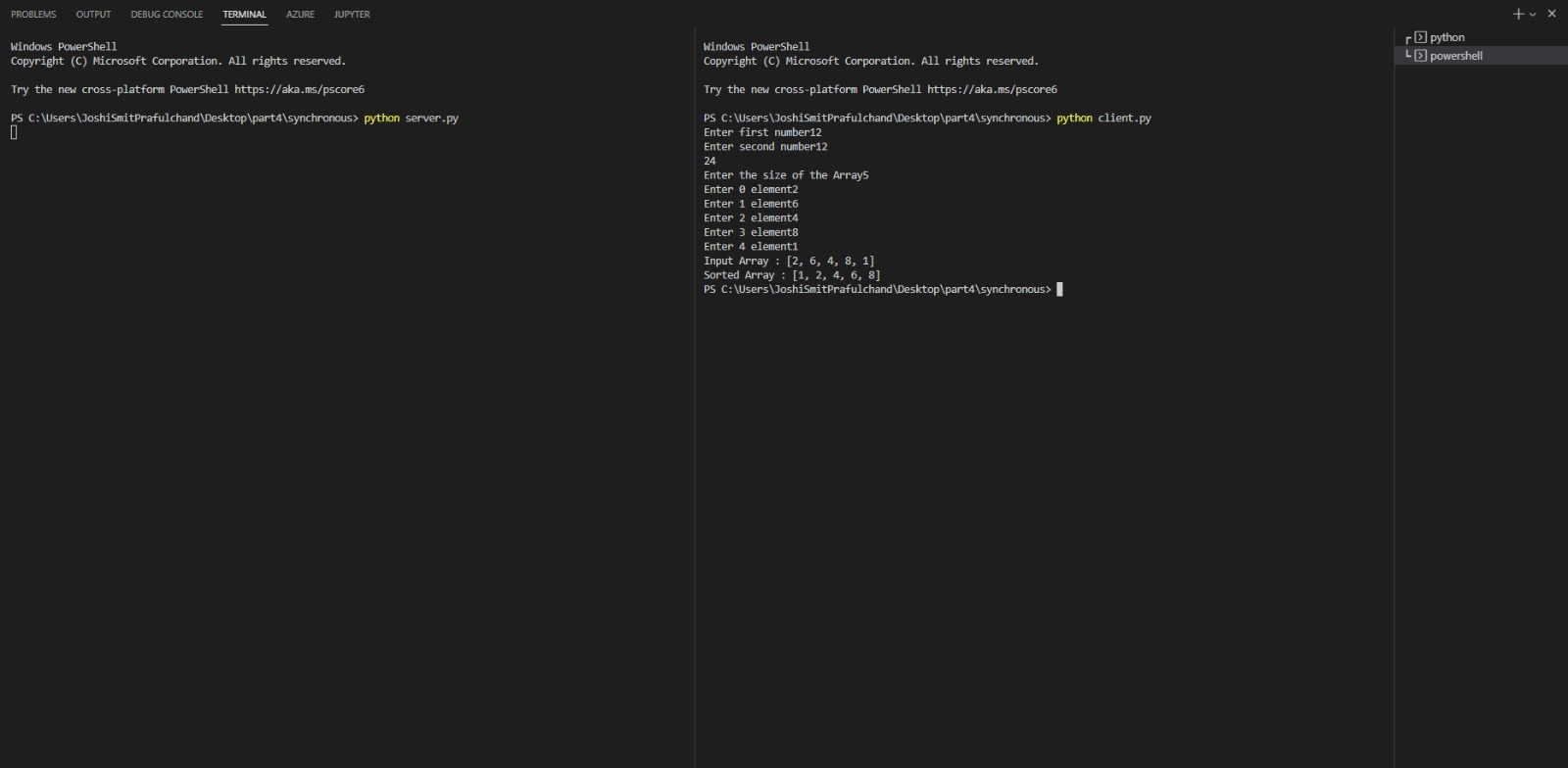
Step 1: Go to project directory and start one command prompt and use command:
python server.py
Step 2: Start another command prompt and use the following command and wait while it perform RPC call
python client.py
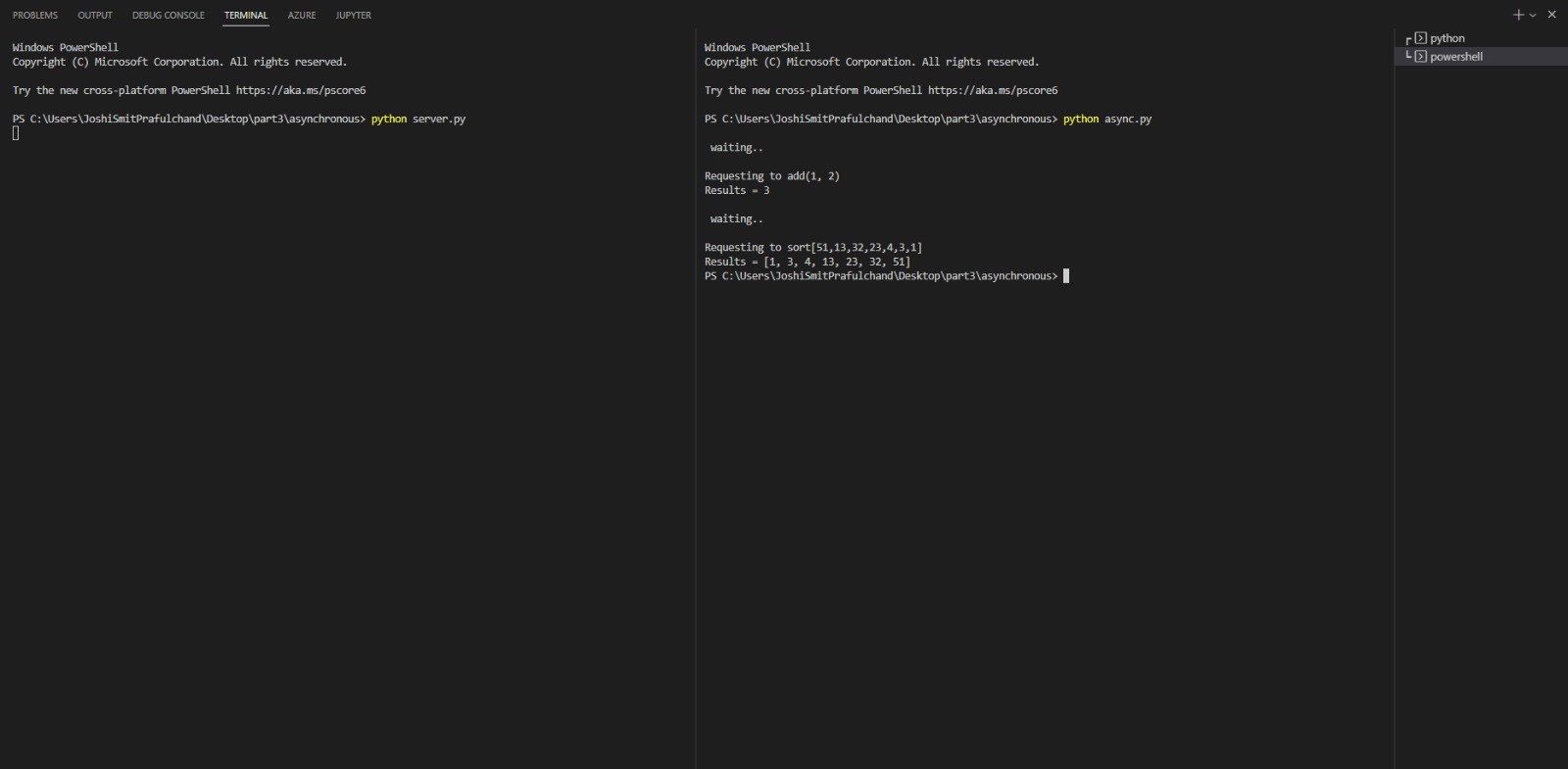
Step 1: Go to project directory and start command prompt and use command:
python server.py
Step 2: Start another command prompt and use following command and wait while it perform RPC call
python async.py
- Synchronous RPC Operations: The client sends a request to the server and waits for the response, ensuring step-by-step, orderly execution.
- Asynchronous RPC Operations: The client does not need to wait for the server's computation to finish. It continues executing other tasks, enhancing efficiency and reducing idle time.
- Basic Computation Tasks: The server can perform addition of two numbers and sort an array, showcasing its ability to handle different types of operations.
- Error Handling: The server effectively communicates error messages in case of any issues during execution.
- Result Retrieval: In asynchronous mode, the client can retrieve the result of the computation once it's complete.
- Python: The project is implemented entirely in Python, taking advantage of its simplicity and versatility.
- Sockets: Python's socket module is used for creating server and client sockets, allowing for communication over the network.
- JSON: JSON is used for encoding and decoding the data that is sent between the client and server.
- Threading (in the case of the asynchronous part): Python's threading module is used to allow for multiple operations to run concurrently.
- Random (in the case of the asynchronous part): Python's random module is used to generate unique tokens for each asynchronous computation request.