|
| 1 | +## Summary |
| 2 | +### General Motivation |
| 3 | + |
| 4 | +The current node affinity feature is relatively simple, it can only affinity with one node. |
| 5 | +Many general functions cannot be supported. |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | +Current node affinity feature don't support functions: |
| 8 | +1. Don't support affinity to a batch of nodes. Current only support affinity to one node. |
| 9 | +2. Don't support anti-affinity to a node of a batch of nodes. |
| 10 | +3. Don't support to classify nodes by labels, and then affinity or anti-affinity to a certain type of nodes. |
| 11 | +4. Don't support affinity/anti-affinity to nodes by node ip or node name. Current only support node id identification. |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +This REP is to solve the above problems. |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | + |
| 16 | +### Should this change be within `ray` or outside? |
| 17 | + |
| 18 | +Yes, this will be a complement to ray core's ability to flexibly schedule actors/tasks/node. |
| 19 | + |
| 20 | +## Stewardship |
| 21 | +### Required Reviewers |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +@ericl @stephanie-wang @wumuzi520 SenlinZhu @Chong Li @scv119 (Chen Shen) @jjyao (Jiajun Yao) @Yi Cheng |
| 24 | +### Shepherd of the Proposal (should be a senior committer) |
| 25 | + |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +## Design and Architecture |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | +### Brief idea |
| 30 | +1. Introduct the concept of the static labels of nodes. Add static labels to nodes(only be set on node start), used to classify nodes. Labels(key, value) = Map<String, String> |
| 31 | +2. Improve the expression of NodeAffinity to support affinity\anti-affinity and labels expressions. |
| 32 | +3. The actual principle of NodeAffinitySchedulingStratgy is. According to the label matching expression in the strategy, traverse and search for LabelsResource of all nodes. Pick out nodes that meet the expression requirements. |
| 33 | + |
| 34 | + |
| 35 | +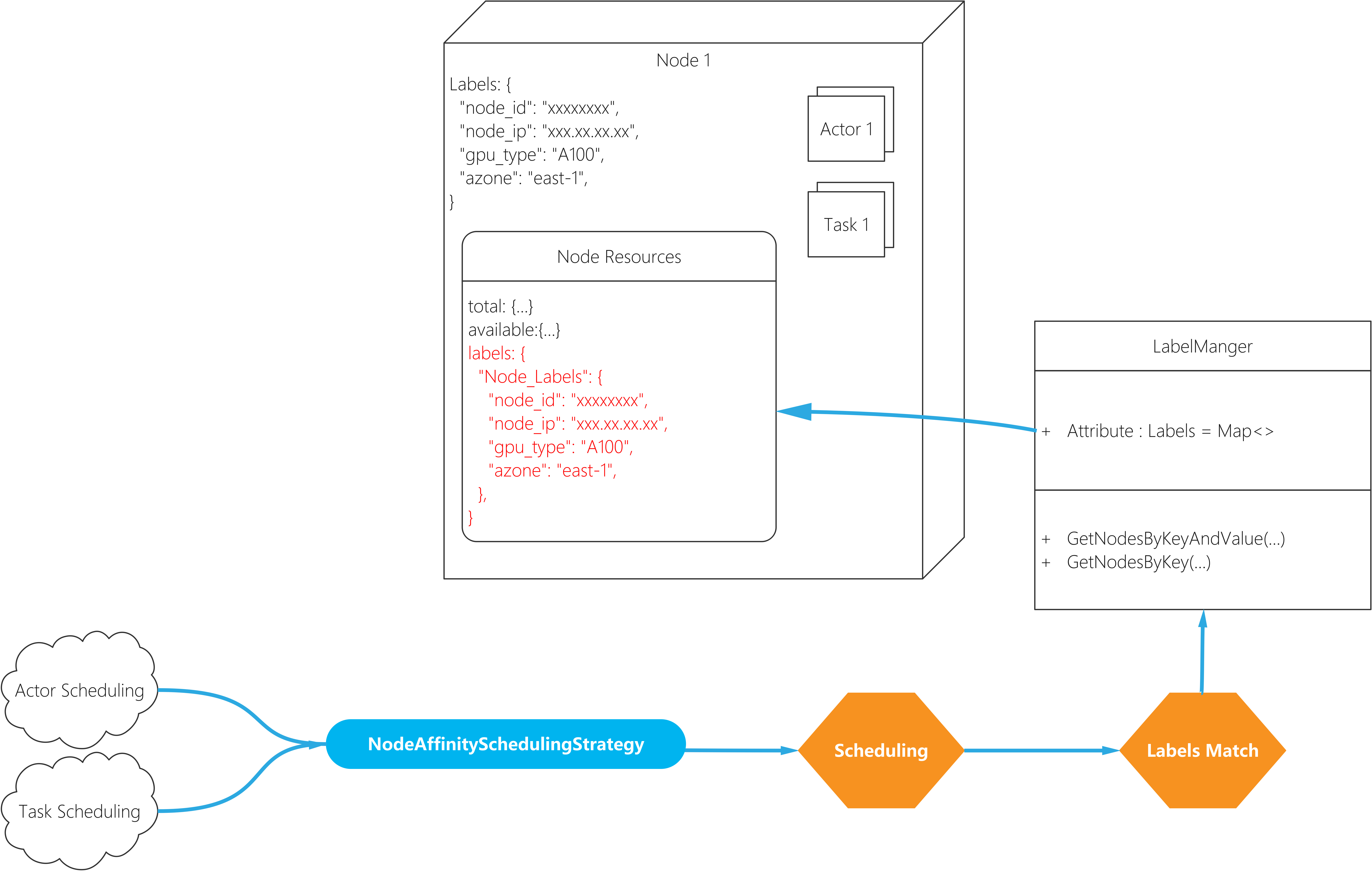 |
| 36 | + |
| 37 | +Scheduling Policy | Label Owner | Label select operator |
| 38 | +-- | -- | -- |
| 39 | +NodeAffinity | Node | in, not_in, exists, does_not_exist |
| 40 | + |
| 41 | +### API Design |
| 42 | + |
| 43 | +**The apis of actors/nodes add labels** |
| 44 | +This interface is already very simple, so we will not set up multiple solutions for everyone to discuss. |
| 45 | +```python |
| 46 | +# Node add static labels. |
| 47 | +ray start ... --labels={"location": "dc_1"} |
| 48 | + |
| 49 | +# Dynamically updating node labels is not implemented now, and will be considered in the second stage. |
| 50 | +``` |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +**The apis of the actor-affinity/node-affinity scheduling.** |
| 53 | + |
| 54 | +**Option 1: Simplify through syntactic sugar** |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +```python |
| 58 | +# Scheduled to a node with a specific IP. |
| 59 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 60 | + scheduling_strategy=node_affinity(label_in(key="node_ip", values=["xxx.xxx.xx.xx"], is_soft=false)) |
| 61 | + ).remote() |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | +# Try to schedule to the node with A100/P100 graphics card. If not, schedule to other nodes. |
| 64 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 65 | + scheduling_strategy=node_affinity(label_in("gpu_type", ["A100", "P100"], is_soft=true)) |
| 66 | + ).remote() |
| 67 | + |
| 68 | +# Do not schedule to the two nodes whose node id is "xxxxxxx"\"aaaaaaaa". |
| 69 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 70 | + scheduling_strategy=node_affinity(label_not_in("node_id", ["xxxxxxx", "aaaaaaaa"], is_soft=false)) |
| 71 | + ).remote() |
| 72 | + |
| 73 | +# Schedule to the node with the key label exist "gpu_type". |
| 74 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 75 | + scheduling_strategy=node_affinity(label_exist("gpu_type")) |
| 76 | + ).remote() |
| 77 | + |
| 78 | +# Don't schedule to the node with the key label exist "gpu_type". |
| 79 | +object_ref = Task.options( |
| 80 | + scheduling_strategy=node_affinity(label_does_not_exist("gpu_type", is_soft=false)) |
| 81 | + ).remote() |
| 82 | + |
| 83 | +# Multiple label expressions can be filled in at the same time, and the relationship between the expressions is "and". The dispatch must satisfy each expression. |
| 84 | +# The actual meaning of this expression is that it must be scheduled to a node with a GPU, and as much as possible to a node with a GPU of the A100 type. |
| 85 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 86 | + scheduling_strategy=node_affinity([ |
| 87 | + label_in("gpu_type", ["A100"], true), |
| 88 | + label_exists("gpu_type", false) |
| 89 | + ]) |
| 90 | + ).remote() |
| 91 | + |
| 92 | +# Note: This api is old. The old api will still be kept for compatibility with old users. |
| 93 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 94 | + scheduling_strategy=NodeAffinitySchedulingStrategy( |
| 95 | + node_id=ray.get_runtime_context().node_id, |
| 96 | + soft=False, |
| 97 | + ) |
| 98 | +).remote() |
| 99 | + |
| 100 | +def node_affinity(...): |
| 101 | + ... |
| 102 | + return NodeAffinitySchedulingStrategy(...) |
| 103 | + |
| 104 | +def label_in(key, values, is_soft=false): |
| 105 | + ... |
| 106 | + return LabelMatchExpression(...) |
| 107 | + |
| 108 | +def label_not_in(key, values, is_soft=false): |
| 109 | + ... |
| 110 | + return LabelMatchExpression(...) |
| 111 | + |
| 112 | +def label_exists(key, is_soft=false): |
| 113 | + ... |
| 114 | + return LabelMatchExpression(...) |
| 115 | + |
| 116 | +def label_does_not_exist(key, is_soft=false): |
| 117 | + ... |
| 118 | + return LabelMatchExpression(...) |
| 119 | + |
| 120 | +``` |
| 121 | + |
| 122 | +**Option 2: another syntactic sugar** |
| 123 | + |
| 124 | +Personally, I think this Option is not as good as the above Option 1. |
| 125 | +The label_in(key, values, is_soft) form of option 1 is more understandable and better than the form of ("location", LabelMatchOperator.IN, ["dc_1"], false). |
| 126 | +```python |
| 127 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 128 | + scheduling_strategy=NodeAffinity([ |
| 129 | + ("node_ip", LabelMatchOperator.IN, ["xxx.xxx.xx.xx"], is_soft=false), |
| 130 | + ).remote() |
| 131 | + |
| 132 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 133 | + scheduling_strategy=NodeAffinity([ |
| 134 | + ("node_id", LabelMatchOperator.NOT_IN, ["xxxxxxx", "aaaaaaaa"], is_soft=true), |
| 135 | + ).remote() |
| 136 | + |
| 137 | +object_ref = Task.options( |
| 138 | + scheduling_strategy=NodeAffinity([ |
| 139 | + ("gpu_type", LabelMatchOperator.IN, ["A100"], is_soft=true), |
| 140 | + ("gpu_type", LabelMatchOperator.Exist)). |
| 141 | + ).remote() |
| 142 | +``` |
| 143 | + |
| 144 | +**Option 3: Java-like form** |
| 145 | + |
| 146 | +This form is similar to Java's syntax. The downside is that it's a bit complicated. |
| 147 | +```python |
| 148 | +SchedulingStrategyT = Union[None, str, |
| 149 | + PlacementGroupSchedulingStrategy, |
| 150 | + NodeAffinitySchedulingStrategy] |
| 151 | + |
| 152 | +class NodeAffinitySchedulingStrategy: |
| 153 | + def __init__(self, match_expressions: List[LabelMatchExpression]): |
| 154 | + self.match_expressions = match_expressions |
| 155 | + |
| 156 | +class LabelMatchExpression: |
| 157 | + """An expression used to select instance by instance's labels |
| 158 | + Attributes: |
| 159 | + key: the key of label |
| 160 | + operator: IN、NOT_IN、EXISTS、DOES_NOT_EXIST, |
| 161 | + if EXISTS、DOES_NOT_EXIST, values set [] |
| 162 | + values: a list of label value |
| 163 | + soft: ... |
| 164 | + """ |
| 165 | + def __init__(self, key: str, operator: LabelMatchOperator, |
| 166 | + values: List[str], soft: bool): |
| 167 | + self.key = key |
| 168 | + self.operator = operator |
| 169 | + self.values = values |
| 170 | + self.soft = soft |
| 171 | + |
| 172 | +actor_1 = Actor.options(scheduling_strategy=NodeAffinitySchedulingStrategy([ |
| 173 | + LabelMatchExpression( |
| 174 | + "node_ip", LabelMatchOperator.IN, ["xxx.xxx.xx.xx"], False) |
| 175 | + ])).remote() |
| 176 | + |
| 177 | +actor_1 = Actor.options(scheduling_strategy=NodeAffinitySchedulingStrategy([ |
| 178 | + LabelMatchExpression( |
| 179 | + "gpu_type", LabelMatchOperator.IN, ["A100"], True), |
| 180 | + LabelMatchExpression( |
| 181 | + "gpu_type", LabelMatchOperator.EXISTS, None, False) |
| 182 | + ])).remote() |
| 183 | +``` |
| 184 | + |
| 185 | +**Option 4: Like sql** |
| 186 | + |
| 187 | +This solution is not recommended. |
| 188 | +This method needs to parse SQL, and the workload will be much larger. |
| 189 | +And users often write wrong sql when using it. |
| 190 | +```python |
| 191 | +# NodeAffinity use case |
| 192 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 193 | + scheduling_strategy=NodeAffinity("gpu_type in [A100, T100]") |
| 194 | + ).remote() |
| 195 | +``` |
| 196 | + |
| 197 | +### Example |
| 198 | + |
| 199 | +**1. Affinity to the node of the specified Instance.** |
| 200 | +``` |
| 201 | +# m6in.2xlarge 8C32G instance node |
| 202 | +ray start ... --labels={"instance": "m6in.2xlarge"} |
| 203 | + |
| 204 | +# m6in.large 2C8G instance node |
| 205 | +ray start ... --labels={"instance": "m6in.large"} |
| 206 | + |
| 207 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 208 | + scheduling_strategy=node_affinity(label_in(key="instance", values=["m6in.large"], is_soft=false)) |
| 209 | + ).remote() |
| 210 | + |
| 211 | +``` |
| 212 | + |
| 213 | +**2. Anti-Affinity to the nodes of the special node_id.** |
| 214 | +``` |
| 215 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 216 | + scheduling_strategy=node_affinity(label_not_in(key="node_id", values=["xxxxx", "aaaaa"], is_soft=false)) |
| 217 | + ).remote() |
| 218 | +``` |
| 219 | + |
| 220 | +**3. Anti-Affinity to the node which have GPU.** |
| 221 | +``` |
| 222 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 223 | + scheduling_strategy=node_affinity(label_does_not_exist(key="gpu_type", is_soft=false)) |
| 224 | + ).remote() |
| 225 | +``` |
| 226 | + |
| 227 | +**4. It must be scheduled to a node whose region is china, and as much as possible to a node whose availability zone is china-east-1.** |
| 228 | + |
| 229 | +``` |
| 230 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 231 | + scheduling_strategy=node_affinity([ |
| 232 | + label_in("region", ["china"], is_soft=false), |
| 233 | + label_in("zone", ["china-east-1"], is_soft=true) |
| 234 | + ]) |
| 235 | + ).remote() |
| 236 | +``` |
| 237 | +**5. NodeAffinity can be used together with the CustomResource mechanism.** |
| 238 | +These two mechanisms are completely non-conflicting. |
| 239 | +``` |
| 240 | +actor_1 = Actor.options( |
| 241 | + num_gpus=1, |
| 242 | + resources={"custom_resource": 1}, |
| 243 | + scheduling_strategy=node_affinity([ |
| 244 | + label_exist("gpu_type", is_soft=false), |
| 245 | + label_in("gpu_type", ["A100", "P100"], is_soft=true), |
| 246 | + ]).remote() |
| 247 | +``` |
| 248 | + |
| 249 | +**FAQ:** |
| 250 | +This node static labels seems to be very similar to custom_resources. Why not use custom_resources to instance of node_affinity? |
| 251 | + |
| 252 | +1. The semantics of static labels and custom_resources are completely different. custom_resources is a countable resource for nodes. And labels is an attribute or identifier of a node. |
| 253 | +2. Now custom_resources cannot implement the function of anti-affinity. |
| 254 | +3. Using labels to classify nodes and implement affinity/anti-affinity will be more natural and easier for users to accept. |
| 255 | + |
| 256 | +### Implementation plan |
| 257 | + |
| 258 | + |
| 259 | + |
| 260 | +1. Add the labels to node info |
| 261 | +``` |
| 262 | +message GcsNodeInfo { |
| 263 | + // The ID of node. |
| 264 | + bytes node_id = 1; |
| 265 | + ... |
| 266 | + // The user-provided identifier or name for this node. |
| 267 | + string node_name = 12; |
| 268 | + // The static labels of nodes. |
| 269 | + map<String, String> labels = 13; |
| 270 | +} |
| 271 | +``` |
| 272 | +2. Add the labels data structure to the resource synchronization data structure(NodeResources). |
| 273 | +``` |
| 274 | +NodeResources { |
| 275 | + ResourceRequest total; |
| 276 | + ResourceRequest available; |
| 277 | + /// Only used by light resource report. |
| 278 | + ResourceRequest load; |
| 279 | + /// Resources owned by normal tasks. |
| 280 | + ResourceRequest normal_task_resources |
| 281 | + /// Map<label_type, Map<namespace, Map<label_key, label_value>>> Nodes labels information |
| 282 | + absl::flat_hash_map<string, absl::flat_hash_map<string, absl::flat_hash_map<string, string>>> labels; |
| 283 | +} |
| 284 | +``` |
| 285 | + |
| 286 | +3. When a node registers with GCS and broadcasts to all nodes, add the static labels information to NodeResources. |
| 287 | + |
| 288 | +Because NodeInfo originally had a mechanism to synchronize to the entire cluster. So there is no need to modify too much code. |
| 289 | + |
| 290 | +4. Scheduling optimization through Labels |
| 291 | + |
| 292 | +Now any node raylet has node static labels information for all nodes. |
| 293 | +when NodeAffinity schedules, if it traverses the Labels of each node, the algorithm complexity is very large, and the performance will be poor. |
| 294 | +<b> Therefore, it is necessary to generate a full-cluster node labels index table to improve scheduling performance. </b> |
| 295 | + |
| 296 | +The label index table is only used to obtain which nodes have this key and value. The complexity of this algorithm is O(1). |
| 297 | +The matching logic of the expression is as follows: |
| 298 | +> label_in(key, values[]) = LabelManager.GetNodesByKeyAndValue() |
| 299 | + |
| 300 | +> label_not_in(key, values[]) = All_Nodes - LabelManager.GetNodesByKeyAndValue() |
| 301 | + |
| 302 | +``` |
| 303 | +class ClusterLabelManager { |
| 304 | + public: |
| 305 | + absl::flat_hash_set<NodeID> GetNodesByNodeKeyAndValue(const std::string &key, const absl::flat_hash_set<std::string> &values) const; |
| 306 | + |
| 307 | + absl::flat_hash_set<NodeID> GetNodesByNodeKey(const std::string &key) const; |
| 308 | + |
| 309 | + void AddNodeLabels(const std::shared_ptr<NodeInfo> &node); |
| 310 | + |
| 311 | + void RemoveNodeLabels(const std::shared_ptr<NodeInfo> &node); |
| 312 | + |
| 313 | + private: |
| 314 | + <namespace, <label_key, <lable_value, [node_id]>>> labels_to_nodes_; |
| 315 | + <node_id, [labels]>> nodes_to_labels_; |
| 316 | +} |
| 317 | +``` |
| 318 | + |
| 319 | + |
| 320 | +### how other system achieve the same goal? |
| 321 | +1、K8s |
| 322 | +This solution is to learn the PodAffinity/NodeAffinity features of K8s。 |
| 323 | +https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/scheduling-eviction/assign-pod-node/#affinity-and-anti-affinity |
| 324 | + |
| 325 | +Scheduling Policy | Label Owner | Operator |
| 326 | +-- | -- | -- |
| 327 | +nodeAffinity | NODE | In, NotIn, Exists, DoesNotExist, Gt, Lt |
| 328 | +podAffinity | POD | In, NotIn, Exists, DoesNotExist |
| 329 | +podAntiAffinity | POD | In, NotIn, Exists, DoesNotExist |
| 330 | + |
| 331 | + |
| 332 | +### what's the alternative to achieve the same goal? |
| 333 | +** Option 3: putting Labels into the custom resource solution ** |
| 334 | +``` |
| 335 | +class ResourceRequest { |
| 336 | + absl::flat_hash_map<ResourceID, FixedPoint> resources_; |
| 337 | +} |
| 338 | + |
| 339 | +Add Actor/Task/Node labels to resources_ as custom resources. |
| 340 | +eg: |
| 341 | +{ |
| 342 | + "CPU": 16, |
| 343 | + "memory": xx, |
| 344 | + "custom_resources": xx, |
| 345 | + "actor_labels_key@value": 1, |
| 346 | + "task_labels_key@value": 1, |
| 347 | + "node_labels_key@value": 1, |
| 348 | +} |
| 349 | +``` |
| 350 | +If you put labels into custom_resources, you need to do the following adaptation: |
| 351 | +1. Compared with custom_resources, labels need to add a specific prefix to distinguish them from custom_resources. |
| 352 | +2. The key and value of Labels need to be concatenated with special characters (@). |
| 353 | +3. When using Labels to build a Labels index table, you need to parse the resources key. |
| 354 | + |
| 355 | +**DisAdvantages:** |
| 356 | +1. Labels unlike cpu resource these are numeric types. Compared with the above scheme. This will destroy the concept of coustrom resouce. |
| 357 | +2. Actor and Task are isolated by namespace. It is difficult to isolate through namespace if adding custom_resource. |
| 358 | +2. The Label index table of all nodes can be constructed from the ActorLabels information of each node. If you use Custom Resource, this requires parsing the resource_key and doing a lot of string splitting which will cost performance. |
| 359 | +3. If custom_resource happens to be the same as the spliced string of labels. Then it will affect the correctness of scheduling. |
| 360 | + |
| 361 | +### AutoScaler adaptation |
| 362 | +I understand that the adaptation of this part of AutoScaler should not be difficult. Now NodeAffinity is just one more scheduling strategy. Just follow the existing implementation of AutoScaler and adapt to the current strategy. |
| 363 | + |
| 364 | +1. Now AutoScaler has an information synchronization interface, just add a labels field. |
| 365 | + |
| 366 | +2. AutoScaler adapts to the NodeAffinity policy. Then some specific behaviors can be determined later. |
| 367 | + |
| 368 | + |
| 369 | +**Nodes:** |
| 370 | +Now Ray has more and more scheduling strategies. If AutoScaler still simulates the scheduling again according to the current implementation method, then code maintenance will become more and more troublesome. For each additional scheduling strategy, AutoScaler needs to be adapted once, which is obviously unreasonable. So I think AutoScaler is still in urgent need of refactoring. |
| 371 | + |
| 372 | +## Compatibility, Deprecation, and Migration Plan |
| 373 | + |
| 374 | +## Test Plan and Acceptance Criteria |
| 375 | +All APIs will be fully unit tested. All specifications in this documentation will be thoroughly tested at the unit-test level. The end-to-end flow will be tested within CI tests. Before the beta release, we will add large-scale testing to precisely understand scalability limitations and performance degradation in large clusters. |
| 376 | + |
| 377 | +## (Optional) Follow-on Work |
| 378 | + |
| 379 | +### 1. Expression of "OR" semantics. |
| 380 | +Later, if necessary, you can extend the semantics of "OR" by adding "is_or_semantics" to ActorAffinitySchedulingStrategy. |
| 381 | +``` |
| 382 | +class NodeAffinitySchedulingStrategy: |
| 383 | + def __init__(self, match_expressions: List[LabelMatchExpression], is_or_semantics = false): |
| 384 | + self.match_expressions = match_expressions |
| 385 | + self.is_or_semantics = |
| 386 | +``` |
| 387 | + |
| 388 | +### 2. Support dynamic updating of node labels. |
| 389 | +The current node label is static (only set when the node is started), and then the node label is dynamically updated through the interface. |
0 commit comments