Releases: codehs/chs-js-lib
0.2.8
What's Changed
- Fixes for adding and subtracting vectors by @anderoonies in #94
Full Changelog: 0.2.7...0.2.8
0.2.7
0.2.7
This release has some new features in Vector and 2d noise, as well as some fixes.
Vector
Vector is a new class for working with 2d and 3d vectors. The full documentation is here, but here are some quick examples to get the idea:
This example normalizes a vector so that its magnitude is equal to the radius of the circle.
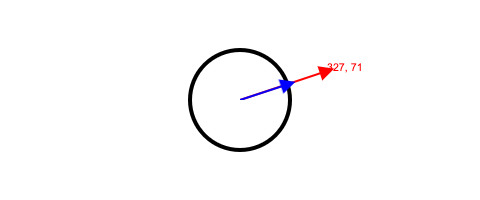
let origin = new Vector(getWidth() / 2, getHeight() / 2);
let mouseVector = new Vector(mouseX, mouseY).subtract(origin);
let normal = mouseVector.clone().normalize().multiply(radius);https://codehs.github.io/chs-js-lib/examples/datastructures/vector/normalize/
This example adds two vectors to produce a third:
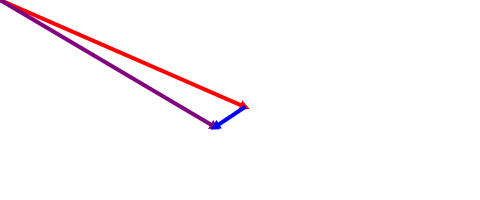
let origin = new Vector(0, 0);
let v1 = new Vector(mouseX, mouseY);
let v2 = new Vector(-30, 20);
draw(origin, v1, 'red');
let v3 = v1.copy().add(v2);
draw(origin, v3, 'purple');
draw(v1, v2, 'blue');https://codehs.github.io/chs-js-lib/examples/datastructures/vector/add/
These examples can be found at https://codehs.github.io/chs-js-lib/examples/.
2d Noise
Randomizer.noise will now return 2 dimensional Perlin noise if it receives a second argument.

setBackgroundColor('white');
for (let row = 0; row < getHeight(); row++) {
for (let col = 0; col < getWidth(); col++) {
const scaledRow = row * 0.02;
const scaledCol = col * 0.02;
const pxl = new Rectangle(1, 1);
pxl.setPosition(col, row);
const n = Randomizer.noise(scaledCol, scaledRow);
pxl.setColor(Color.createFromRGB(n * 255, n * 255, n * 255));
add(pxl);
}
}https://codehs.github.io/chs-js-lib/examples/randomizer/2dnoise/
Fixes
- Rotation calculations are only performed if an element has non-zero rotation, which is a performance gain in some cases.
- Lines rotated in Groups have been fixed by making sure that the width and height of a line are distance, rather than potentially negative vectors.
Full Changelog: 0.2.6...0.2.7
0.2.6
This release is a small fix for making sure setFullscreen() behaves similarly to setSize regarding resolution for devicePixelRatio calculations
0.2.5
Improvements
Resolution
This release adds improvements for displaying graphics on devices that have >1 pixel density, meaning they use more than one physical pixel to draw a graphical pixel. For example, retina displays have a 2:1 device pixel ratio. To make the most of this, the library draws at double size, then is shrunk back down using CSS. This lets the library provide as much data as possible, and will result in crisper visuals, especially with rounded objects and Text.
Cleanup
Graphics instances now have a cleanup method which will remove their event listeners from the window
Performance
Accessible DOM elements created when adding graphics elements are now lazy-created when the user first hits Tab to enter keyboard navigation mode. This improves performance on very large programs with a lot of graphical elements.
Fixes
- Remove keyboard navigable DOM elements when the underlying Thing is removed by @anderoonies in #73
- Safely bail from getX and getY if no touches are present in a TouchEvent, which happens on touchend by @anderoonies in #82
- Explicitly begin and close paths for WebImages by @anderoonies in #83
- Remove keyboard navigable DOM elements when the underlying Thing is removed by @anderoonies in #73
Full Changelog: 0.2.4...0.2.5
0.2.4
0.2.4 brings accessibility improvements with keyboard navigation and screen reader support, as well as some bug fixes.
Keyboard Navigation
Elements added to the drawing canvas will respond to keyboard navigation with the tab key, just like other DOM elements. Hitting the tab key will flip between elements in the canvas, and screen readers will pick up on descriptions of the elements.
The canvas now has two modes, one that supports keyboard navigation and one that doesn't. Switching between these modes should be seamless. Hitting tab while the canvas has focus will enter this mode, and moving the mouse will exit this mode.
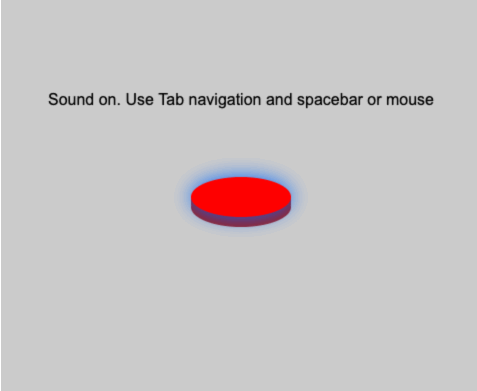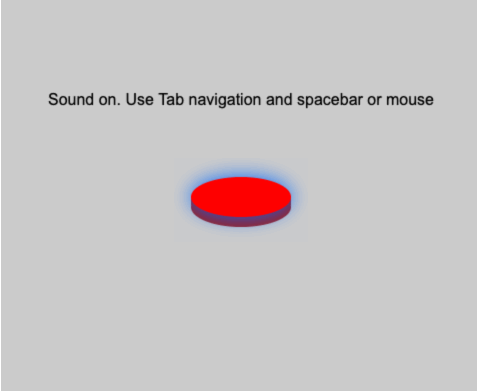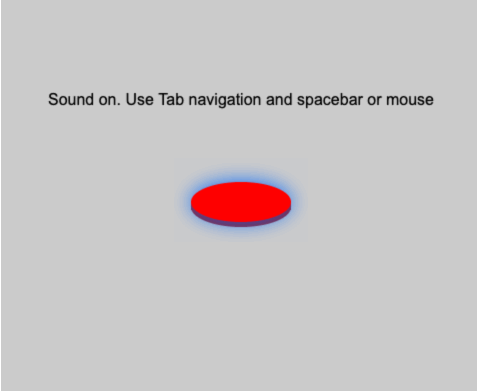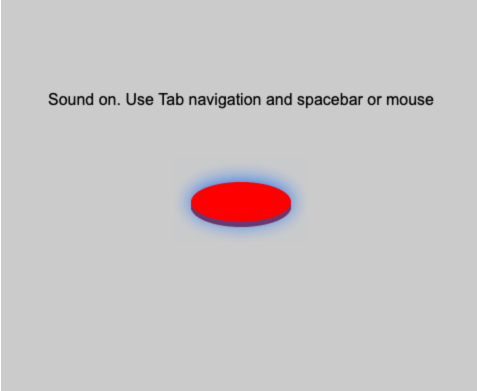
While an element has focus, pressing the spacebar will fire any callback registered with mouseDownMethod a
t the (x, y) position of the focused element, and unpressing the spacebar will fire any callback registered with mouseUpMethod.
See this example, where I'm hitting the spacebar with the button focused:
Elements are described to screen readers according to the describe method. If you ever subclass an element, you can write your own describe function that will describe the element. For example:
class Ghost extends Thing {
describe() {
return `A scary ghost located at ${this.x}, ${this.y}`.
}
}Fixes
- Fixes an issue where WebImages would be cropped when scaled down (#67)
- When updating the font of Text, recalculate size by (#64)
- Respect layering of elements when drawing in Groups by @anderoonies in #70
Full Changelog: 0.2.3...0.2.4
0.2.3
This release fixes .remove, which was incorrectly causing all elements to cascade delete.
0.2.2
GitHub Actions troubleshooting for not including dist/ in releases.
0.2.0
Fixes a bug where dist/ was not included in published package.
See previous release notes!
0.2.0
0.2.0 Brings a lot of features and fixes!
Groups
Groups are a new class that allows for multiple elements to be joined and operated on as a unit. After joining elements in a group, move, setPosition, and rotate/setRotation on the group will affect all elements.
For example, the following code produces the following output:
const group = new Group();
const r = new Rectangle(40, 40);
r.setPosition(50, 50);
r.rotate(45);
const c = new Circle(30);
c.setPosition(50, 50);
group.add(r);
group.add(c);
group.debug = true;
add(group);This required a lot of internal changes to Thing, specifically adding set and get for any attribute that would change an element's position.
You can see the value of Groups in making an example like this:
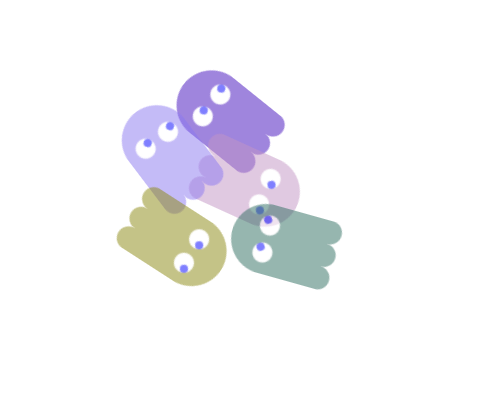

Each ghost is rotated as a group and has its opacity set as a group.
Anchors
Anchors are an extrapolation of an existing concept in the library which allow you to define how an object should be draw relative to its position.
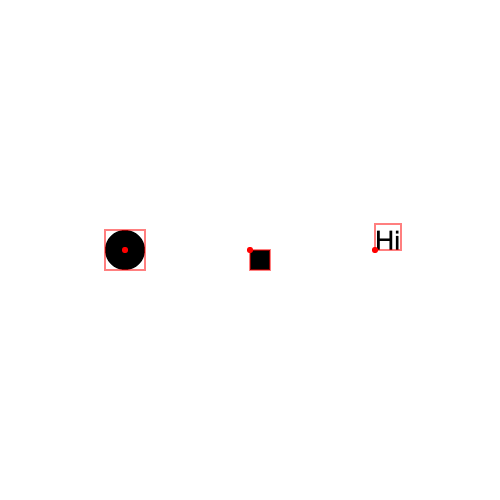
There's already the implicit behavior that most things draw from their top left corner, with the exception of Circle, Oval, Arc, and Text. For reference, consider this example:
c = new Circle(20);
c.debug = true;
c.setPosition(getWidth() / 4, getHeight() / 2);
add(c);
const r = new Rectangle(20, 20);
r.debug = true;
r.setPosition(2 * getWidth() / 4, getHeight() / 2);
add(r);
const t = new Text("Hi");
t.debug = true;
t.setPosition(3 * getWidth() / 4, getHeight() / 2);
add(t);In debug mode (more on that later), you can see that the Circle is drawn with its position at its center, the Rectangle (square) is drawn with its position at its top left, and the Text is drawn with its position at the bottom left.
This has been extracted into the more general form anchor = {vertical: 0...1.0, horizontal: 0...1.0}. An element's anchor has a vertical and horizontal component, each a float from 0 to 1 that describes where it should be drawn relative to its position. A Circle has a default anchor of {vertical: 0.5, horizontal: 0.5}, a Rectangle has a default anchor of {vertical: 0, horizontal: 0}, and Text has a default anchor of {vertical: 1, horizontal: 0}.
The anchor of an element can be changed with setAnchor, and allows you to describe how an elements should be drawn relative to its position.
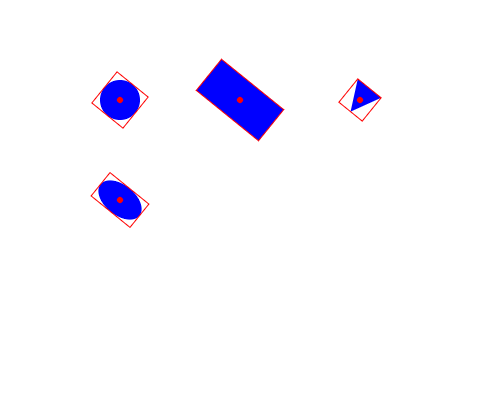
For example, here are three circles, with anchors {vertical: 0, horizontal: 0}, {vertical: 0.5, horizontal: 0.5} (default), and {vertical: 1, horizontal: 1}:
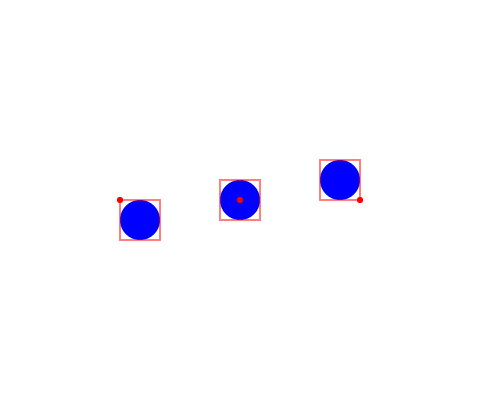
All elements support anchoring, as well as Groups, which are anchored just the same:
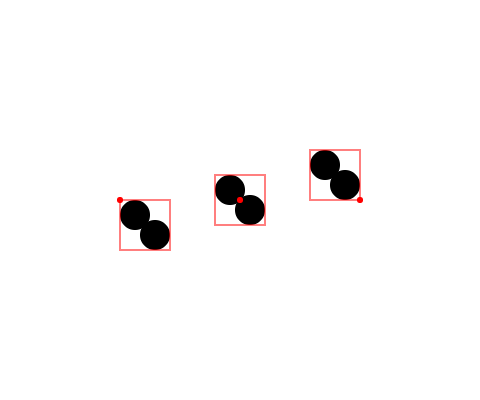
Elements will still be rotated around their center as before, regardless of anchoring.
Debug
Elements now have the property .debug, which is false by default, and controls whether debug information should be drawn with the element. When .debug is true, the element's bounds and position will be drawn on the screen as a red box and a red circle. Groups and elements all have a debug mode, which function the same.
Noise
A noise function produces continuous random values, as opposed to a function like Math.random() which will produce non-continous values. noise has been added to the Randomizer module as Randomizer.noise, a function that takes a number and produces a float from 0 to 1. Because it is continuous, Randomizer.noise(x) for continuous x values will also be continuous.
Map
map is exposed in the global namespace as a function that takes a value and its current range and re-maps it to a target range. For example, map(x, 0, 100, 0, 255) would remap x from the range 0-100 to the range 0-255. map(50, 0, 100, 0, 255) will produce 127.5.
This example maps the square distance from the mouse's position, a number from 0 to 900, to an alpha value from 0 to 255:

Fixes and Improvements
containsPointcalculations now account for the rotation of the element- Expose a
getElementsAtfunction which returns all elements at the x and y coordinate - Simplify Oval internals with the
ellipsefunction - Correct Polygon height and width calculations
- Immediately fire
loadedcallback functions on WebImage if they're registered after the WebImage has already loaded - Improve performance when adding and removing large numbers of elements by lazy-removing elements from the element pool
0.1.18
Hotfix for uses ECMAScript Modules.
What's Changed
- ESModules, not CJS by @anderoonies in #50
Full Changelog: 0.1.17...0.1.18