|
| 1 | +--- |
| 2 | +title: Heroku Application Logs Integration Guide |
| 3 | +description: Forward Heroku application logs to OpenObserve using a forwarding app to parse Logplex syslogs into structured JSON. |
| 4 | +--- |
| 5 | + |
| 6 | +# Integration with Heroku Application Logs |
| 7 | + |
| 8 | +This guide explains how to stream Heroku application logs—including app, router, error, and system logs—into OpenObserve using a forwarding app that parses Logplex syslogs into structured JSON. |
| 9 | + |
| 10 | +## Overview |
| 11 | + |
| 12 | +Heroku’s Logplex consolidates logs from your app (stdout/stderr), router (HTTP requests), and system events (dyno restarts). While convenient, it’s limited by retention length (1,500 lines or one week) and raw text format, which is hard to analyze. |
| 13 | + |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | + |
| 16 | +OpenObserve ingests these logs in structured JSON format, enabling fast search, rich visualization, and proactive alerting. |
| 17 | + |
| 18 | +## Steps to Integrate |
| 19 | + |
| 20 | +??? "Prerequisites" |
| 21 | + - OpenObserve account ([Cloud](https://cloud.openobserve.ai/web/) or [Self-Hosted](../../../quickstart/#self-hosted-installation)) |
| 22 | + - **An existing Heroku application** already deployed and generating logs |
| 23 | + - Heroku CLI installed and authenticated |
| 24 | + - Node.js, npm, Git, and terminal access |
| 25 | + |
| 26 | +??? "Step 1: Retrieve OpenObserve Endpoint and Credentials" |
| 27 | + |
| 28 | + 1. In OpenObserve: go to **Data Sources → Custom → Logs** → Syslog-NG section |
| 29 | +  |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | + 2. Keep the credentials handy.Construct the Heroku-specific ingestion endpoint: |
| 32 | + ``` |
| 33 | + https://api.openobserve.ai/api/<organization_id>/<stream_name/_json |
| 34 | + ``` |
| 35 | + |
| 36 | +??? "Step 2: Build a Forwarding App to Parse and Send Logs" |
| 37 | + |
| 38 | + 1. Initialize a new forwarding app: |
| 39 | + ```bash |
| 40 | + mkdir heroku-log-forwarder |
| 41 | + cd heroku-log-forwarder |
| 42 | + npm init -y |
| 43 | + npm install express body-parser node-fetch@2 |
| 44 | + ``` |
| 45 | + |
| 46 | + 2. Create `index.js` and paste: |
| 47 | + |
| 48 | + ```javascript |
| 49 | + const express = require('express'); |
| 50 | + const bodyParser = require('body-parser'); |
| 51 | + const fetch = require('node-fetch'); |
| 52 | + |
| 53 | + const app = express(); |
| 54 | + app.use(bodyParser.text({ type: '*/*' })); |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | + const OPENOBSERVE_URL = 'https://api.openobserve.ai/api/<organization_id>/heroku_logs/_json'; |
| 57 | + const OPENOBSERVE_USER = '[email protected]'; |
| 58 | + const OPENOBSERVE_PASS = 'your_password'; |
| 59 | + |
| 60 | + const logRegex = /^(\d+) <\d+>1\s+([\d-:.+]+)\s+host\s+(\w+)\s+(\w+)\.(\d+)\s*-\s*(.*)$/; |
| 61 | + const routerRegex = /^(\d+) <\d+>1\s+([\d-:.+]+)\s+host\s+heroku\s+(\w+)\s*-\s+at=info\s+(.*)$/; |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | + app.post('/logs', async (req, res) => { |
| 64 | + const rawLogs = req.body.split('\n').filter(log => log.trim()); |
| 65 | + const enriched = rawLogs.map(log => { |
| 66 | + let match = log.match(logRegex); |
| 67 | + if (match) { |
| 68 | + const [, , timestamp, source, dynoNum, dynoId, message] = match; |
| 69 | + return { |
| 70 | + app: "your-heroku-app-name", |
| 71 | + dyno: `${dynoNum}.${dynoId}`, |
| 72 | + message, |
| 73 | + source: source.toLowerCase(), |
| 74 | + timestamp |
| 75 | + }; |
| 76 | + } |
| 77 | + match = log.match(routerRegex); |
| 78 | + if (match) { |
| 79 | + const [, , timestamp, source, details] = match; |
| 80 | + const params = details.split(' ').reduce((acc, pair) => { |
| 81 | + const [key, value] = pair.split('='); |
| 82 | + acc[key] = value.replace(/^"(.*)"$/, '$1'); |
| 83 | + return acc; |
| 84 | + }, {}); |
| 85 | + return { |
| 86 | + app: "your-heroku-app-name", |
| 87 | + dyno: params.dyno, |
| 88 | + message: details, |
| 89 | + source: source.toLowerCase(), |
| 90 | + timestamp, |
| 91 | + ...params |
| 92 | + }; |
| 93 | + } |
| 94 | + console.warn(`Unparsed log: ${log}`); |
| 95 | + return { message: log, timestamp: new Date().toISOString() }; |
| 96 | + }); |
| 97 | + |
| 98 | + try { |
| 99 | + const resp = await fetch(OPENOBSERVE_URL, { |
| 100 | + method: 'POST', |
| 101 | + headers: { |
| 102 | + 'Content-Type': 'application/json', |
| 103 | + 'Authorization': `Basic ${Buffer.from(`${OPENOBSERVE_USER}:${OPENOBSERVE_PASS}`).toString('base64')}` |
| 104 | + }, |
| 105 | + body: JSON.stringify(enriched) |
| 106 | + }); |
| 107 | + if (!resp.ok) throw new Error(`Ingestion failed: ${resp.status}`); |
| 108 | + console.log(`Forwarded ${enriched.length} logs`); |
| 109 | + res.sendStatus(200); |
| 110 | + } catch (err) { |
| 111 | + console.error('Error forwarding logs:', err.message); |
| 112 | + res.status(500).send('Forwarding failed'); |
| 113 | + } |
| 114 | + }); |
| 115 | + |
| 116 | + app.listen(process.env.PORT || 3000, () => console.log(`Forwarder running on port ${process.env.PORT || 3000}`)); |
| 117 | + ``` |
| 118 | + |
| 119 | + 3. Update placeholders (`<organization_id>`, credentials, and app name) accordingly |
| 120 | + 4. Create a proc file `web: node index.js` |
| 121 | + 5. Update `package.json` file: |
| 122 | + ```bash |
| 123 | + { |
| 124 | + "name": "heroku-log-forwarder", |
| 125 | + "version": "1.0.0", |
| 126 | + "main": "index.js", |
| 127 | + "scripts": { |
| 128 | + "start": "node index.js" |
| 129 | + }, |
| 130 | + "dependencies": { |
| 131 | + "express": "^4.21.2", |
| 132 | + "body-parser": "^1.20.3", |
| 133 | + "node-fetch": "^2.6.7" |
| 134 | + } |
| 135 | + } |
| 136 | + ``` |
| 137 | + |
| 138 | +??? "Step 3: Deploy Forwarding App to Heroku and Configure Log Drain" |
| 139 | + |
| 140 | + 1. Deploy the forwarding app: |
| 141 | + ```bash |
| 142 | + git init |
| 143 | + git add . |
| 144 | + git commit -m "Heroku log forwarder" |
| 145 | + heroku create heroku-log-forwarder |
| 146 | + git push heroku main |
| 147 | + ``` |
| 148 | + |
| 149 | + Note the deployed URL (e.g., `https://heroku-log-forwarder.herokuapp.com`). |
| 150 | + |
| 151 | + 2. Configure the log drain from your existing app: |
| 152 | + ```bash |
| 153 | + heroku drains:add "https://heroku-log-forwarder.herokuapp.com/logs" -a <your-heroku-app-name> |
| 154 | + ``` |
| 155 | + 3. Optionally, reduce sampling rate if you encounter buffer overflows: |
| 156 | + ```bash |
| 157 | + heroku drains:update --sampling-rate 25 <drain-id> -a <your-heroku-app-name> |
| 158 | + ``` |
| 159 | + 4. Verify drain setup: |
| 160 | + ```bash |
| 161 | + heroku drains -a <your-heroku-app-name> |
| 162 | + ``` |
| 163 | + |
| 164 | +??? "Step 4: Verify Logs in OpenObserve" |
| 165 | + |
| 166 | + 1. In OpenObserve, go to **Logs → heroku_logs** and run a query to see structured entries. |
| 167 | + |
| 168 | + 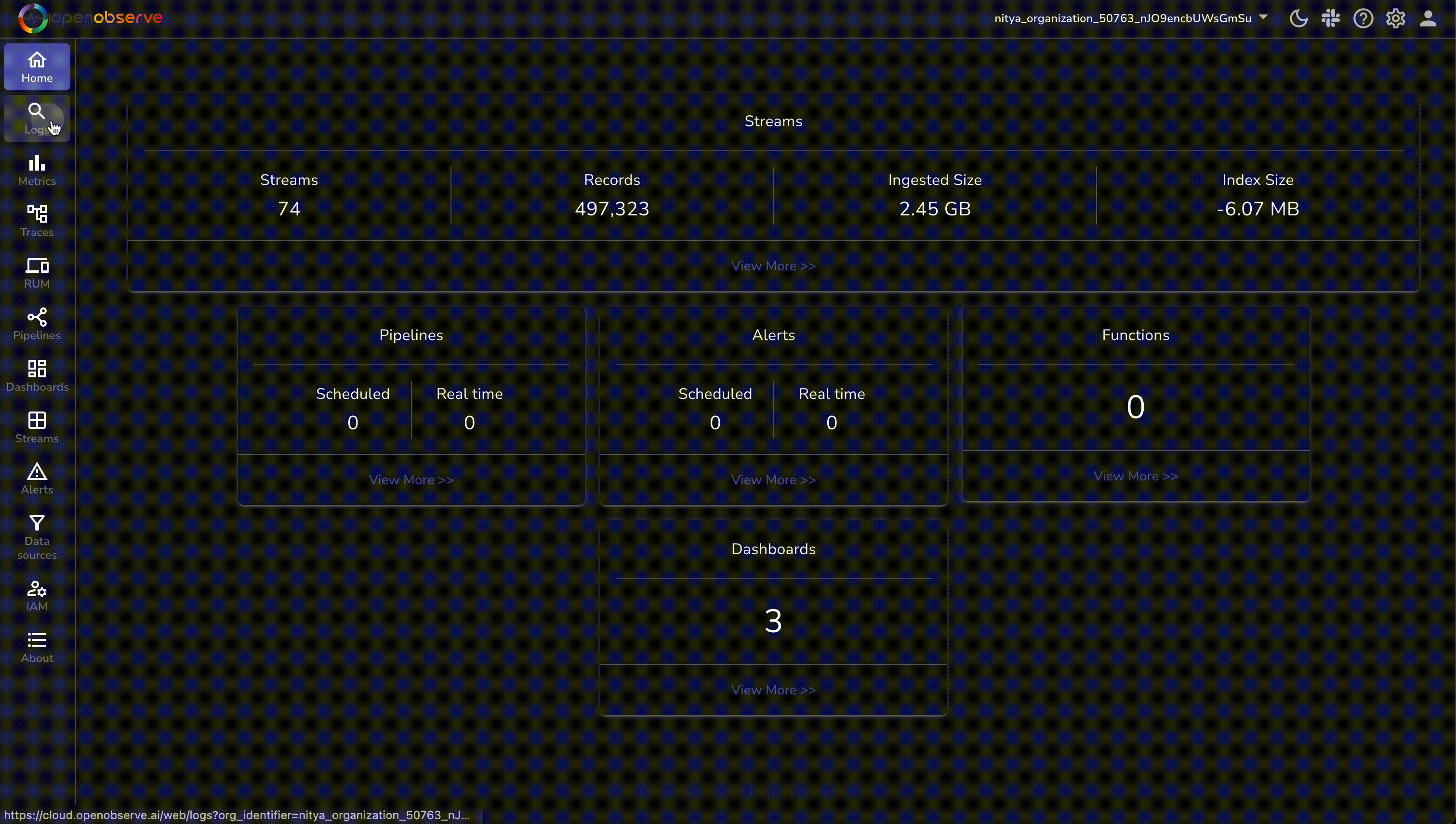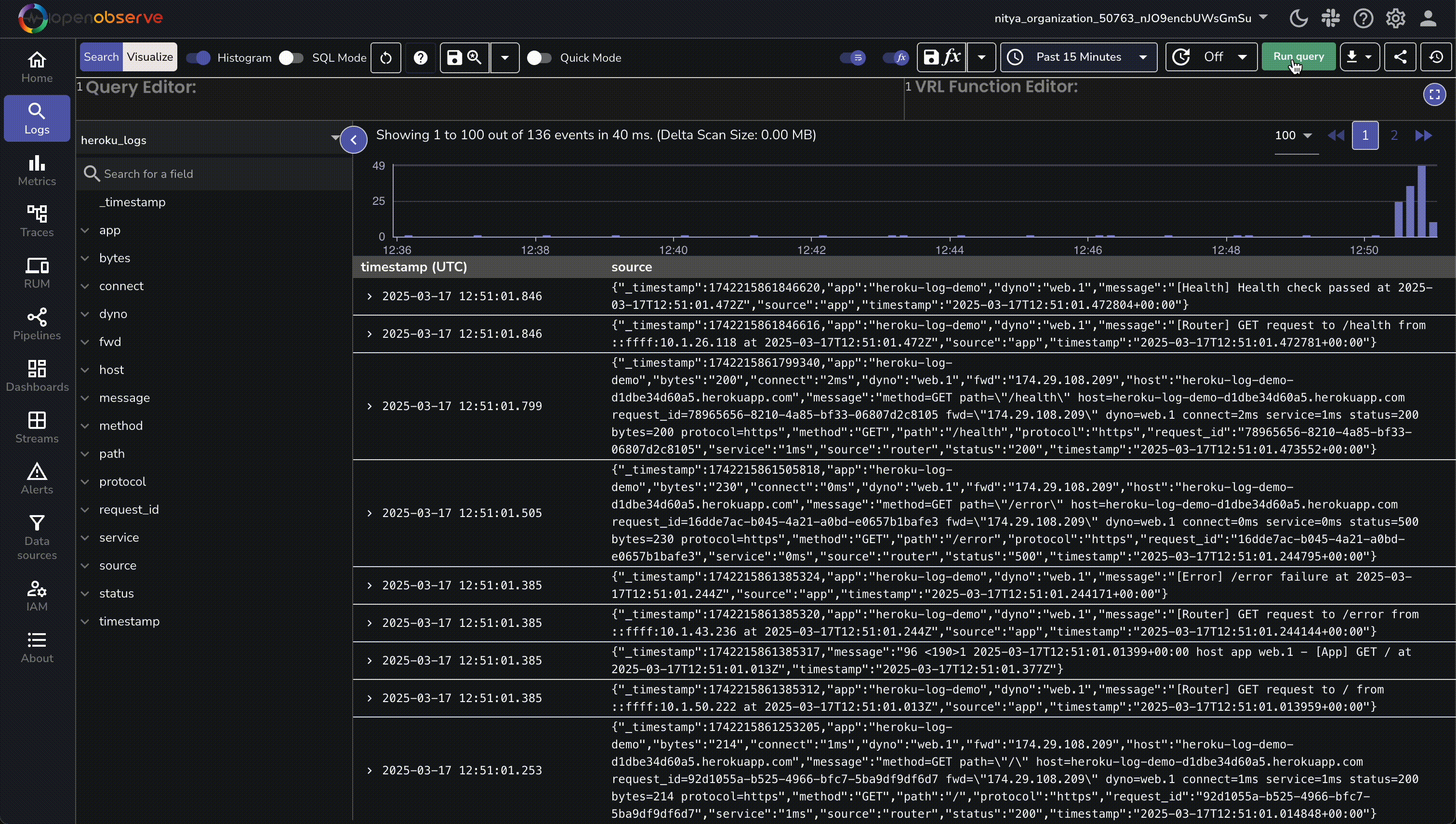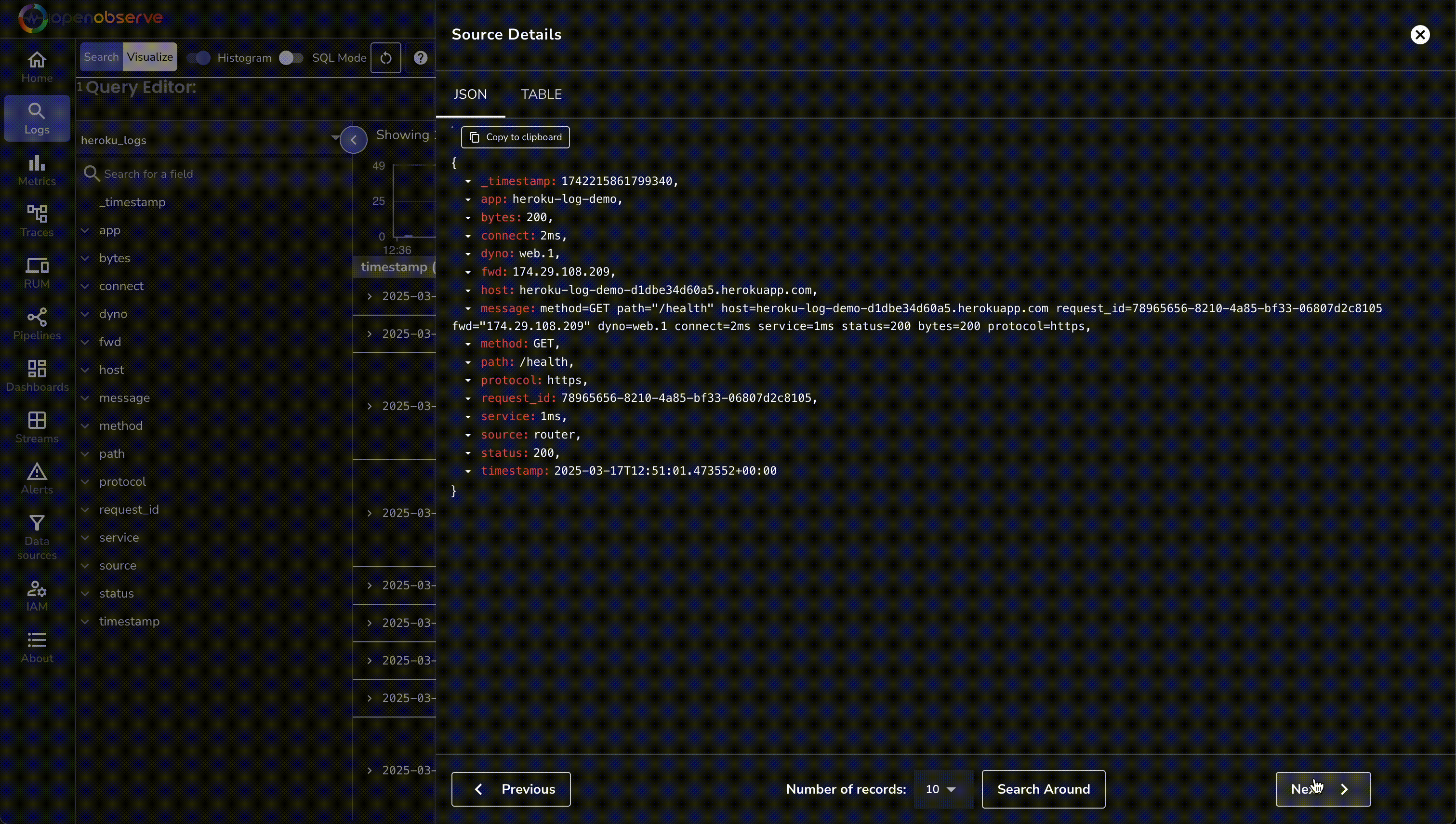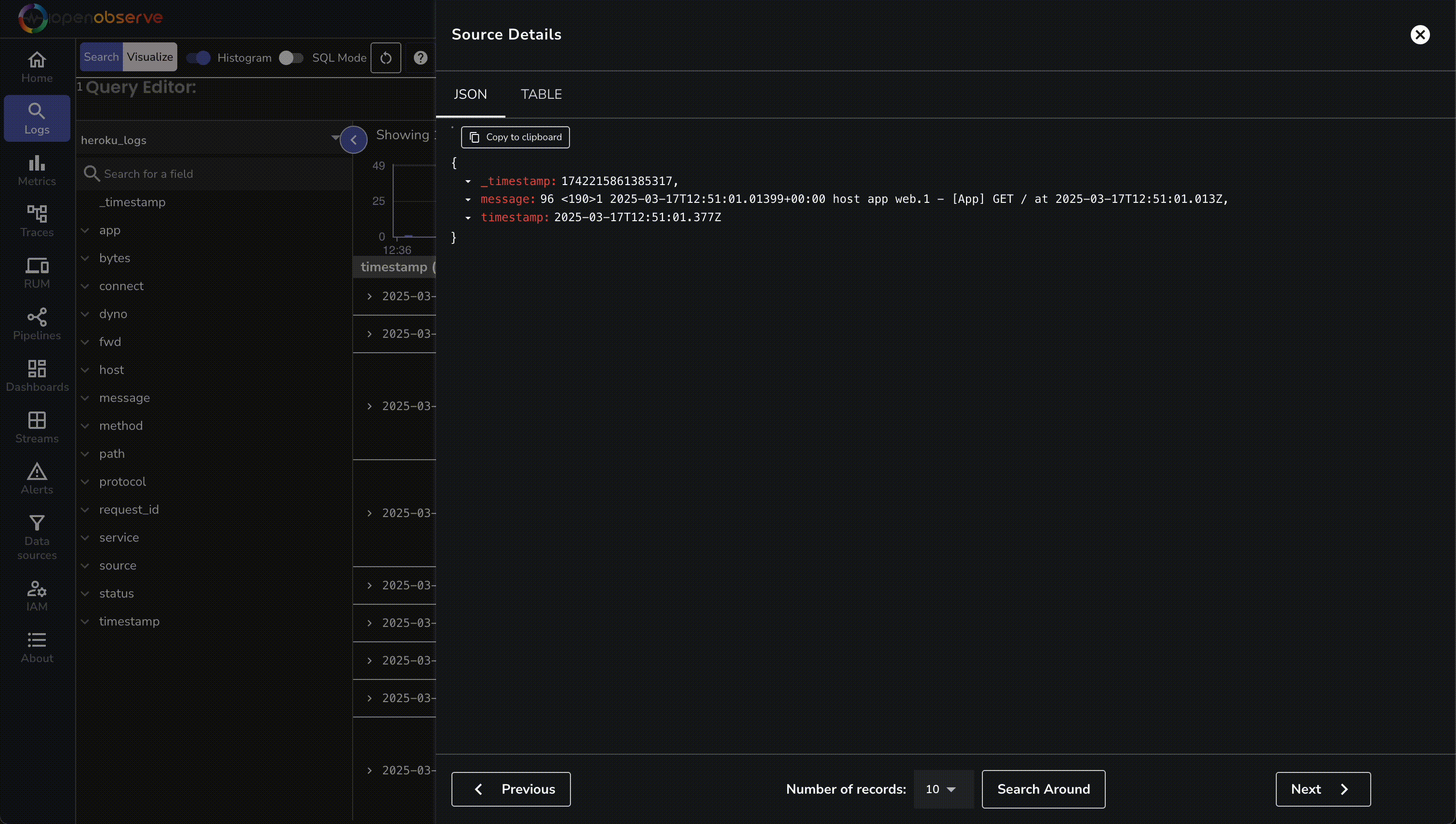 |
| 169 | + |
| 170 | +## Troubleshooting |
| 171 | + |
| 172 | +??? "**No logs or some log types missing**" |
| 173 | + - Check Heroku app logs (More → View logs) to confirm log generation (Router, App, Error types) |
| 174 | + - Confirm the drain is active: |
| 175 | + ```bash |
| 176 | + heroku drains -a <your-heroku-app-name> |
| 177 | + ``` |
| 178 | + - Tail your forwarder logs for warnings or errors |
| 179 | + |
| 180 | +??? "**Buffer overflow (Error L10)**" |
| 181 | + - Reduce sampling rate: |
| 182 | + ```bash |
| 183 | + heroku drains:update --sampling-rate 10 <drain-id> -a <your-heroku-app-name> |
| 184 | + ``` |
| 185 | + |
| 186 | +??? "**Unparsed logs**" |
| 187 | + - Review `Unparsed log` warnings in forwarder logs |
| 188 | + - Adjust regex patterns in `index.js` |
| 189 | + |
| 190 | +??? "**Truncated logs**" |
| 191 | + - Heroku truncates lines >10 KB. Simplify log message content in forwarding app and redeploy |
| 192 | + |
| 193 | +??? "**Slow log delivery**" |
| 194 | + - Increase heartbeat interval in `index.js` or reduce traffic volume |
0 commit comments