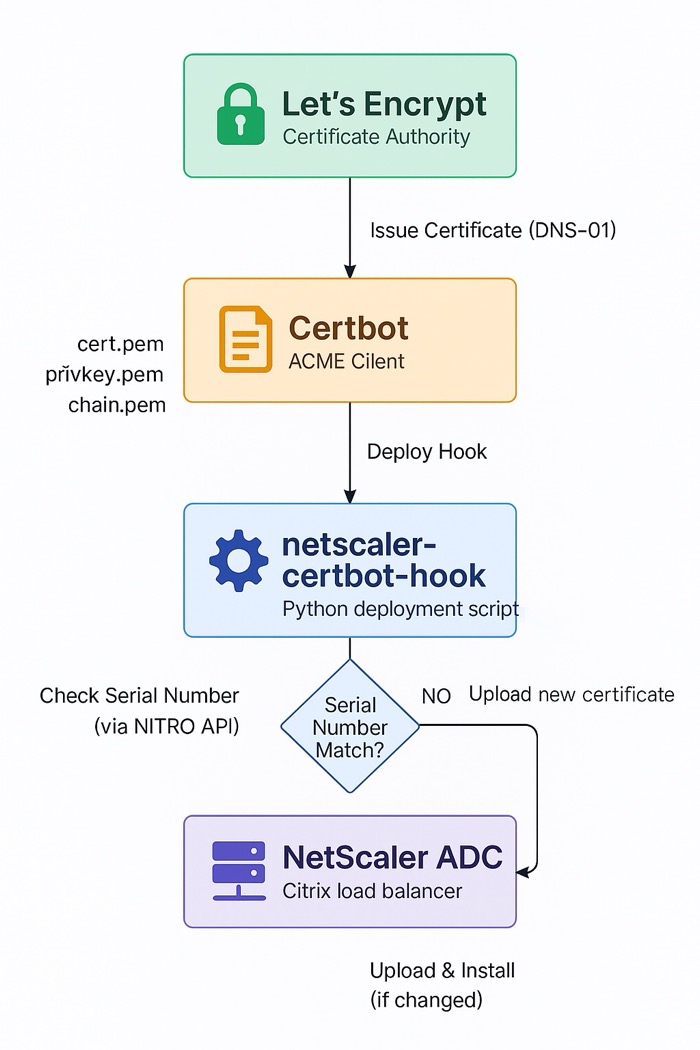
Automated SSL certificate management for Citrix NetScaler ADC. This tool seamlessly integrates with Certbot to install and renew Let's Encrypt certificates on NetScaler appliances via the NITRO API.
Perfect for automating certificate lifecycle management in combination with DNS-01 challenges for fully automated, hands-free certificate renewals.
- ✅ Automated Certificate Installation - Upload and install certificates with a single command
- ✅ Smart Updates - Only updates certificates when serial numbers differ
- ✅ Chain Certificate Handling - Automatic linking to intermediate certificates
- ✅ Configuration Persistence - Automatically saves NetScaler configuration
- ✅ Idempotent Operations - Safe to run repeatedly, only changes when needed
- ✅ Custom Certificate Paths - Supports non-standard certificate locations
- ✅ Comprehensive Validation - Pre-flight checks for files, credentials, and configuration
- ✅ Detailed Error Messages - Clear feedback when something goes wrong
- ✅ Type-Safe - Full type hints for IDE support and static analysis
The script connects to your NetScaler via NITRO API, compares certificate serial numbers, and performs uploads/installations only when necessary. Chain certificates are handled separately for security reasons.
- Python 3.8 or higher
- Citrix NetScaler ADC with NITRO API access
- Certbot (for Let's Encrypt certificate enrollment)
- Network access to NetScaler management interface
# Install directly from PyPI
pip install netscaler-certbot-hookAfter installation, the netscaler-certbot-hook command will be available system-wide.
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/slauger/netscaler-certbot-hook.git
cd netscaler-certbot-hook
# Install in development mode
pip install -e .# For manual script execution
pip install -r requirements.txtpyOpenSSL>=20.0.0- SSL certificate handlingrequests>=2.25.0- NITRO API communication
The script requires the following environment variables:
| Variable | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
NS_URL |
Yes | - | NetScaler management URL (e.g., https://192.168.10.10) |
NS_LOGIN |
No | nsroot |
NetScaler administrator username |
NS_PASSWORD |
No | nsroot |
NetScaler administrator password |
NS_VERIFY_SSL |
No | true |
Verify SSL certificate (true, false, 1, 0) |
Example:
export NS_URL=https://192.168.10.10
export NS_LOGIN=nsroot
export NS_PASSWORD=your-secure-password
export NS_VERIFY_SSL=truenetscaler-certbot-hook --helpNote: If installed from PyPI, use netscaler-certbot-hook. If running from source, use netscaler-certbot-hook or python3 -m netscaler_certbot_hook.
| Argument | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
--name |
Yes | - | Certificate object name on NetScaler |
--chain |
No | Auto-detected from CN | Chain certificate object name (auto-detected from certificate CN if not specified) |
--cert |
No | /etc/letsencrypt/live/<name>/cert.pem |
Path to certificate file |
--privkey |
No | /etc/letsencrypt/live/<name>/privkey.pem |
Path to private key file |
--chain-cert |
No | /etc/letsencrypt/live/<name>/chain.pem |
Path to chain certificate file |
--verbose |
No | false |
Enable verbose output (DEBUG level) |
--quiet |
No | false |
Suppress all output except errors |
--update-chain |
No | false |
Allow updating chain certificate if serial differs |
--no-domain-check |
No | false |
Skip domain validation when updating certificates |
First, obtain a certificate from Let's Encrypt using Certbot with DNS-01 challenge:
certbot --text --agree-tos --non-interactive certonly \
--cert-name 'example.com' \
-d 'example.com' \
-d 'www.example.com' \
-a dns-cloudflare \
--dns-cloudflare-credentials /etc/letsencrypt/cloudflare.ini \
--keep-until-expiring# Route53 (AWS)
certbot certonly --dns-route53 -d example.com
# Google Cloud DNS
certbot certonly --dns-google -d example.com
# Manual DNS (for testing)
certbot certonly --manual --preferred-challenges dns -d example.comnetscaler-certbot-hook --name example.comnetscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com \
--cert /path/to/cert.pem \
--privkey /path/to/privkey.pem \
--chain-cert /path/to/chain.pemBy default, the script automatically detects the chain certificate name from the Common Name (CN) in the certificate. For example, Let's Encrypt intermediate certificates like "R10", "R11", "E5", "E6" etc. are automatically detected:
# Chain name is auto-detected from the certificate CN
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com
# Creates/updates chain certificate with name like "R11" or "E6"You can override the auto-detection and specify a custom chain certificate name:
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --chain my-custom-chain# Enable detailed DEBUG logging
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --verbose# Suppress all output except errors
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --quietWhen trust chains change (e.g., Let's Encrypt issuer switching from E8 to E7), use both --update-chain and --no-domain-check flags:
# Allow chain certificate updates when serial differs
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --update-chain --no-domain-checkNote: By default, the script will refuse to update chain certificates if the serial number differs. This is a security measure to prevent unexpected trust chain changes. Use --update-chain only when you are certain the new chain certificate is valid and expected.
Why --no-domain-check is required: Chain certificates (intermediate CAs) are registered to different domains than your end-entity certificate. Without this flag, NetScaler will reject the update with the error: "Certificate is registered to a different domain; use the 'no domain check' option to force the operation".
The --no-domain-check flag is useful in several scenarios:
# Update certificate with domain changes or multi-domain certificates
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --no-domain-checkWhen to use --no-domain-check:
- Updating chain/intermediate certificates (required)
- Certificates with multiple SANs (Subject Alternative Names)
- Certificates bound to multiple virtual servers
- When domain names in the certificate have changed
- Any scenario where NetScaler reports: "Certificate is registered to a different domain"
Technical Details: This flag passes the nodomaincheck parameter to the NetScaler NITRO API, which bypasses domain validation during certificate updates.
Add to your crontab for automatic renewal:
# Renew certificates daily and update NetScaler
0 3 * * * certbot renew --quiet && netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.comOr create a Certbot deploy hook:
# /etc/letsencrypt/renewal-hooks/deploy/netscaler-hook.sh
#!/bin/bash
export NS_URL=https://192.168.10.10
export NS_LOGIN=nsroot
export NS_PASSWORD=your-password
netscaler-certbot-hook --name $RENEWED_DOMAINSMake it executable:
chmod +x /etc/letsencrypt/renewal-hooks/deploy/netscaler-hook.shThe script uses Python's built-in logging framework for structured output. You can control the verbosity with command-line flags:
| Flag | Log Level | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| default | INFO |
Standard output showing progress |
--verbose |
DEBUG |
Detailed output for troubleshooting |
--quiet |
ERROR |
Minimal output, only errors |
Standard Output (INFO level):
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.comShows all important operations and their status.
Verbose Mode (DEBUG level):
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --verboseShows additional debugging information including:
- Connection details
- Configuration values
- Detailed operation steps
Quiet Mode (ERROR level):
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --quietOnly shows errors. Perfect for cron jobs where you only want to be notified of failures.
For automated cron jobs, use --quiet to suppress normal output:
# Only log errors to file
0 3 * * * netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --quiet 2>> /var/log/netscaler-cert-errors.logOr use standard output with log rotation:
# Log all output with rotation
0 3 * * * netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com >> /var/log/netscaler-cert.log 2>&1When running for the first time:
chain certificate letsencrypt not found
uploading chain certificate as letsencrypt-1581896753.crt
installing chain certificate with serial 13298795840390663119752826058995181320
certificate example.com not found
uploading certificate as example.com-1581896753.crt
uploading private key as example.com-1581896753.key
installing certificate with serial 409596789458967997345847308430335698529007
link certificate example.com to chain certificate letsencrypt
saving configuration
When certificate has been renewed:
chain certificate letsencrypt found with serial 13298795840390663119752826058995181320
installed chain certificate matches our serial - nothing to do
certificate example.com found with serial 409596789458967997345847308430335698529007
uploading certificate as example.com-1581896812.crt
uploading private key as example.com-1581896812.key
update certificate example.com
link certificate example.com to chain certificate letsencrypt
certificate link was already present - nothing to do
saving configuration
When certificate is already up-to-date:
chain certificate letsencrypt found with serial 13298795840390663119752826058995181320
installed chain certificate matches our serial - nothing to do
certificate example.com found with serial 409596789458967997345847308430335698529007
installed certificate matches our serial - nothing to do
By default, the script does not automatically update chain certificates if the serial number differs. This prevents potential security issues from unexpected chain updates.
To enable chain certificate updates, use the --update-chain flag:
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --update-chainWhen to use --update-chain:
- Let's Encrypt issuer rotation (e.g., switching from E8 to E7)
- Let's Encrypt root certificate rotation
- CA intermediate certificate updates
- Planned trust chain migrations
Important: Chain certificate updates typically require both --update-chain (to allow the update) and --no-domain-check (to bypass domain validation). Example:
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --update-chain --no-domain-checkSecurity Warning: Only use --update-chain when you are expecting a chain certificate change and have verified the new certificate is valid. Unexpected chain changes could indicate a security issue.
The --no-domain-check flag tells NetScaler to skip domain validation when updating certificates. This is necessary in several scenarios:
Common use cases:
- Chain certificate updates (required) - Chain certificates are registered to CA domains, not your domain
- Multi-domain certificates - Certificates with multiple SANs may trigger domain validation errors
- Certificate rebinding - Certificates bound to multiple virtual servers
- Domain changes - When updating certificates with modified domain names
Error message this solves:
ERROR: Certificate is registered to a different domain; use the 'no domain check' option to force the operation
Example usage:
# Update chain certificate (both flags required)
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --update-chain --no-domain-check
# Update regular certificate with domain validation issues
netscaler-certbot-hook --name example.com --no-domain-checkTechnical Details: This flag passes the nodomaincheck parameter to the NetScaler NITRO API during certificate update operations.
Never commit credentials to version control! Use environment variables or secure credential management:
# Store in secure location
echo "export NS_PASSWORD='your-password'" > ~/.netscaler-credentials
chmod 600 ~/.netscaler-credentials
# Source when needed
source ~/.netscaler-credentialsAlways enable SSL verification in production:
export NS_VERIFY_SSL=trueOnly disable for testing or development environments.
The script uses the Citrix NetScaler NITRO API. For more information:
See CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines on contributing to this project
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
- Simon Lauger - @slauger
For issues, questions, or contributions, please use the GitHub issue tracker