📑 Project Title
Post Emergency Power Management for IoT based Precision Agriculture Irrigation System
Using Cost-Effective Algorithm and Serverless
📅 Project Period
10-10-2021(SUN) ~ 12-20-2021(MON)
🧖🏻♀️ Problem Statement
The United States has more than 1200 tornadoes per year and almost the highest number of tornadoes in the world.
Especially, these tornadoes incidences mostly occur in the plains region of the US.
The tornado occurence area coincides with a large amount of cropland. When such a natural disaster occurs
the power is cut off, causing a large-scale blackout, and this is not just a problem in cities.
Recently, as smart farms are created by combining agriculture with IoT, most of the farm work is becoming automated.
In this situation, if the electricity is cut off, the operation of automation technology of the smart farm will be damaged,
and the crops will dry while waiting for someone to come and water them.
Therefore, a system that can respond flexibly during a disaster until power is restored is needed.
📖 Considerations
🥕Software : Develop an algorithm that can use less power or use it more efficiently.
🥕Hardware : Change the system configuration so that the system itself can reduce power consumption.
💡 Novelty
1. Develop the existing simple algorithm's concept!
=> We researched about the existing smart farm system that irrigatie automatically using Fuzzy and Genetic Algorithms.
But these were too complicated for us and they only focused on normal situations with stable power.
So we researed about simple algorithm that uses only the soil moisture value as a variable.
We developed this algorithm by adding the remaining amount of power and the distance away from the irrigation source as a variables.
2. Use LoRa, LoRaWAN with Serverless(FaaS)!
=> Most smart farms have implemented wireless network using WiFi, Zigbee, and LoRaWAN to get sensor values.
Wi-Fi was not suitable for our project because it has more delay and more power consumption than LoRa.
And Zigbee, a low-power communication technology, it's not suitable for outdoor farms too, because of its limited to short communication coverage.
So, we decided to use LoRa and LoRaWAN.There were many related research about smart farm using LoRaWAN.
But we want to have more novelty in power saving. So, we used serverless and FaaS which is good way to reduce idle power consumption in our system,
that needs to reduce the time inverval between sending data to the server.
🏛 System Overview
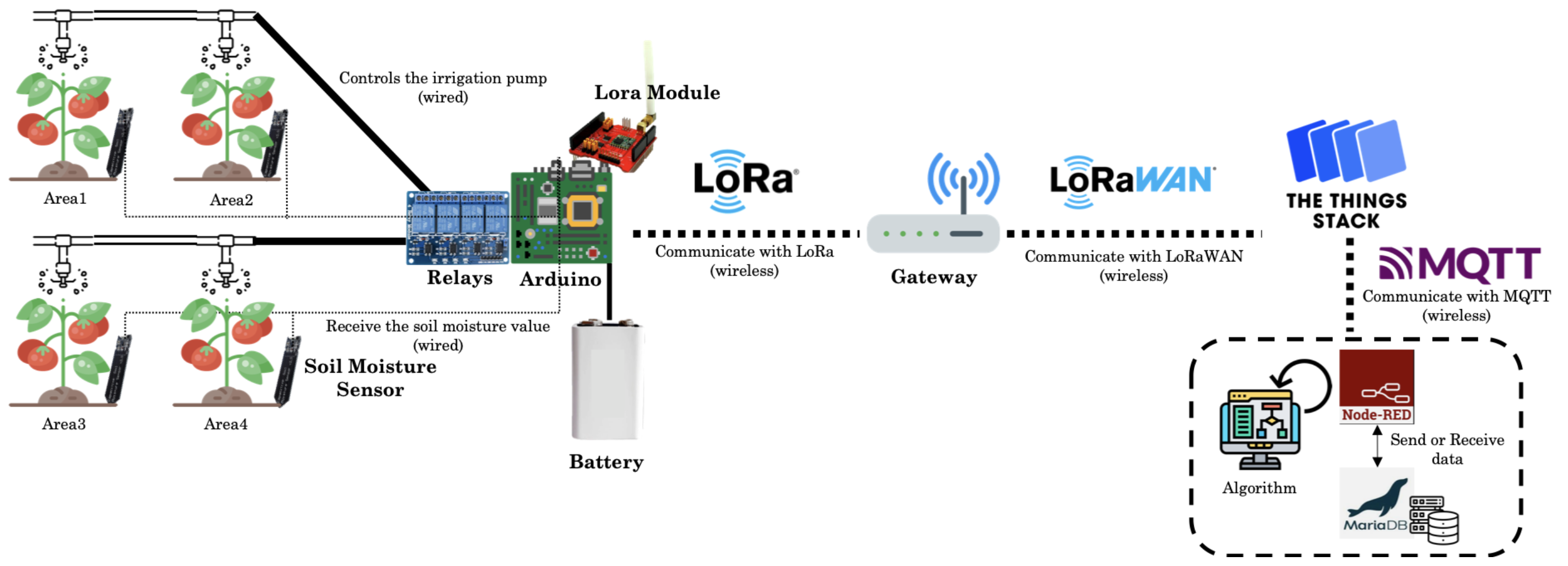
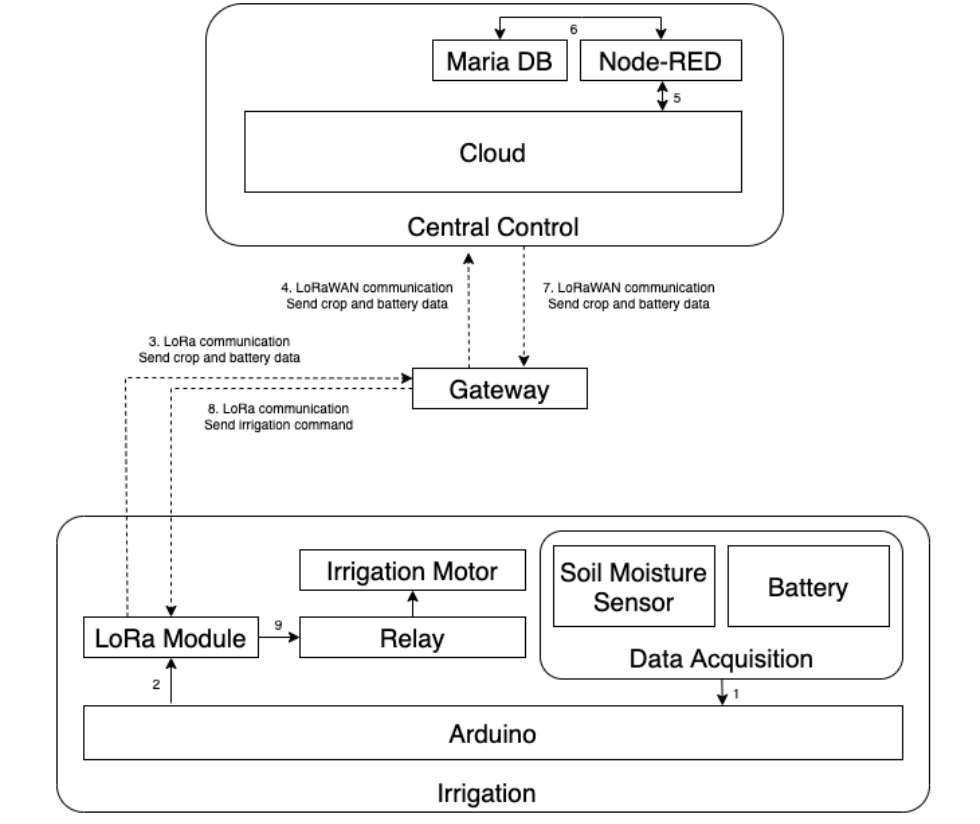
1. Tomatoes were planted in 4 areas, each with a soil moisture sensor and irrigation tube installed.
2. The crop data is transmitted to the gateway through LoRa communication.
3. The gateway sends the crop data to the Cloud through LoRaWAN communication.
4. When the crop data arrives at the Cloud, store it in the database and apply the devised algorithm.
5. The Cloud sends the irrigation command to the gateway.
6. The irrigation command arrives at the Arduino which operates the irrigation system.
🥕Data Acquisition: In this part, soil moisture sensors acquire soil moisture values in tomato fields. The sensor is connected to the Arduino by a wire.
The soil moisture value is delivered as an integer type and 4 values are delivered as an array.
Data on the remaining amount of battery to operate the automatic irrigation system and the acquired crop data are collected on an Arduino connected to the sensor.
The sensor data collected by the Arduino is then transferred to the gateway through LoRa communication.
🥕Central Control: This part is the main part of the project. The collected data from the Data Acquisition Unit arrives at the cloud from the gateway.
It stores the crop data in the database at the time that the data arrives and applies the devised algorithm.
The result of this algorithm, which is an irrigation command, is transmitted to the Arduino.
By using Node-RED in the cloud, the farmer can monitor the data through the Node-RED User Interface (UI) remotely.
🥕Irrigation: This part receives and executes the irrigation command sent from the cloud.
In this part, the motor connected to the water pipe for irrigation is connected to the relay.
The relay connected to the Arduino receives the "turn the motor on and off" command sent from the LoRa module to execute automatic irrigation.
🖥️ Environment Setting
✔️macOS Big Sur version 11.4
✔️Arduino IDE version 1.8.13
✔️Python version 3.7.3
✔️Arduio Uno
✔️LoRa Module : Dragino
✔️Soil Moisture Sensor version 1.2
📤 Installation
$ git clone https://github.com/MINJILEE-PURDUE/KSW_2021_Fall_Program.git
$ cd thomas
👨👩👧👧 Collaborator
👩💻Yujung Gil
-Dongguk Univeristy
-Major in Computer Science Engineering
-kuj9628@naver.com
-https://github.com/fairyroad
🎅🏻Minjeong Kim
-Dongguk University
-Major in Computer Science Engineering
-kimmin9624@dgu.ac.kr
-https://github.com/kimminje0ng
👰Jiho Park
-Dongguk University
-Major in Computer Science Engineering
-jiho8345@dgu.ac.kr
-https://github.com/zihos
👩🚀Bryan Supinski
-Purdue University
-Major in CNIT
-bryansupinski@gmail.com
-https://github.com/dplok1
👨🏻🦱Damien Pham
-Purdue University
-Major in CNIT
-minhduypham0210@gmail.com
-https://github.com/damien7749
👨🏻💼Max Li
-Purdue University
-Major in CNIT
-maxli32145@gmail.com
-https://github.com/Tybolis
🧔🏻Parker Alexander
-Purdue University
-Major in CNIT
-carmelo15andonly@gmail.com
-https://github.com/alexandp1995
[1] Open Source WiFi, Linux Appliance, Dragino. Accessed on: December 02, 2021. [Online]. Available: Dragino