Verifying your Git commits builds trust and shows authenticity. On GitHub, verified commits display a “Verified” badge to signal they were signed with a trusted GPG key.
-
macOS
-
GPG Suite installed (includes GPG Keychain)
-
Git installed
-
GitHub account
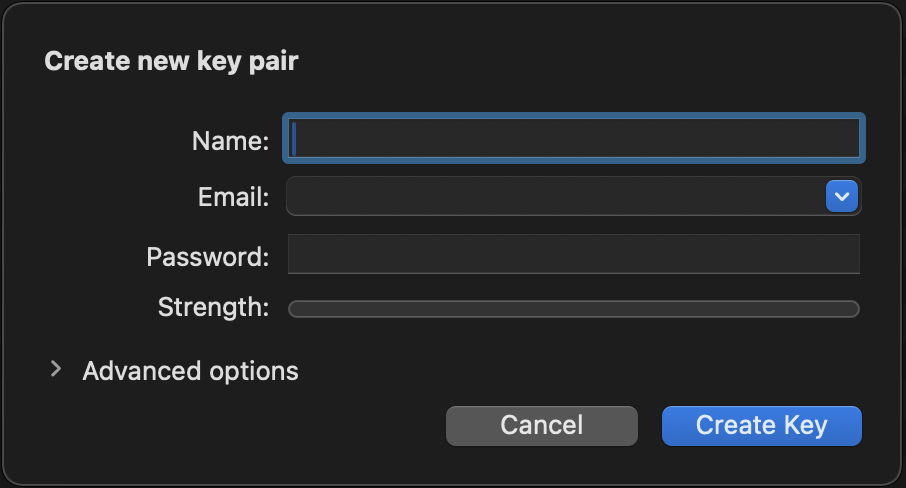
- Name (should match your GitHub name
- Email (must match the email you use in your Git commits)
- Key Type: RSA and RSA (default)
- Key Length: 4096 bits (recommended)
- Expiration date: Optional
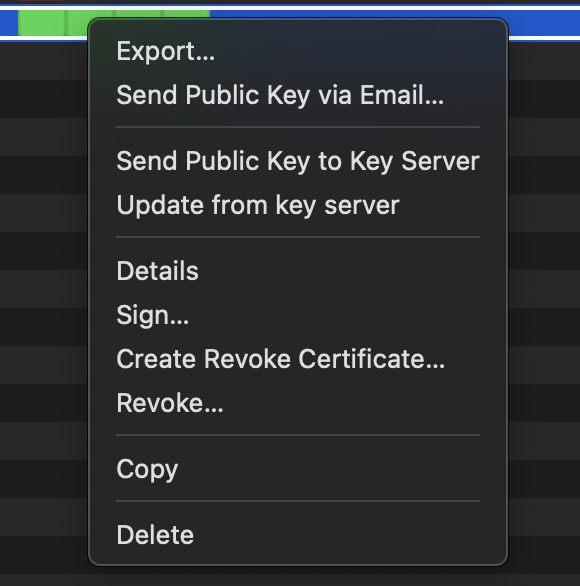
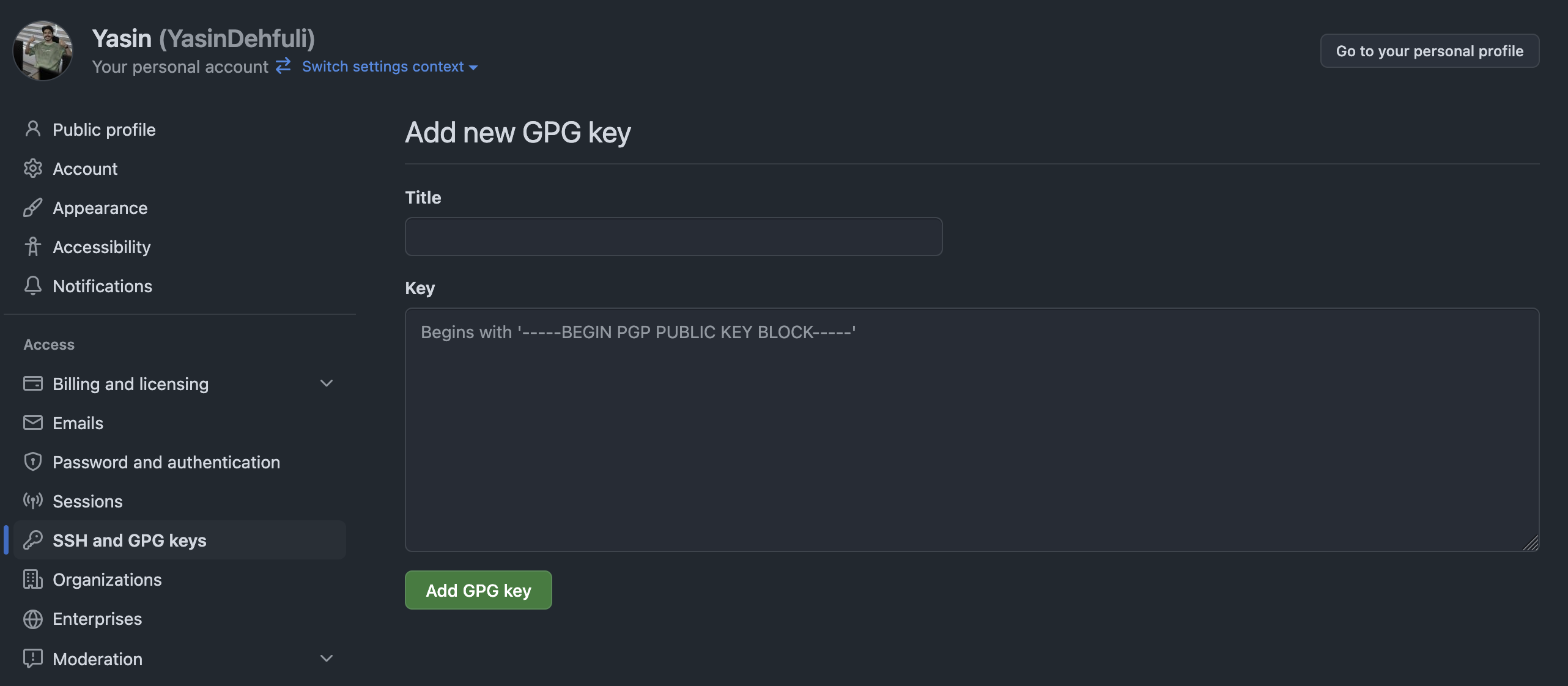
- Go to GitHub → Settings → SSH and GPG Keys.
- Click “New GPG Key”.
- Paste the copied key (or the contents of your exported .asc file).
- Click “Add GPG Key”.
Find your GPG key ID:
gpg --list-secret-keys --keyid-format LONG
Look for the line that looks like this:
sec rsa4096/ABCD1234EFGH5678 ..
Then configure Git:
git config --global user.signingkey ABCD1234EFGH5678
git config --global commit.gpgsign true
Set Git to use GPG (this path may vary):
git config --global gpg.program $(which gpg)
git commit -S -m "Your signed commit message"
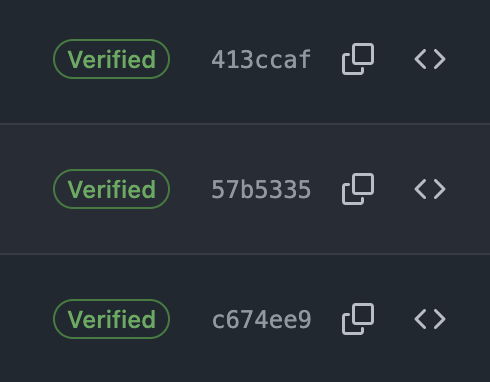
Push your code to GitHub. If everything is set up correctly, GitHub will show a Verified badge next to your commit.
As you can see verified commits of this repository.
If you want to learn how to get GitHub achievements! You can learn it step by step here ==> Get-Github-Achievements-Step-By-Step