OUROBOROS is a research-focused forensic toolkit that analyzes binary executables using a broad set of mathematical, statistical and interdisciplinary methods. It is designed to extract robust, explainable signals (topological, spectral, dynamical, informational) and fuse them into an ensemble verdict for advanced malware and anomaly detection.
Details
Project Details
Technical Details
Algorithms
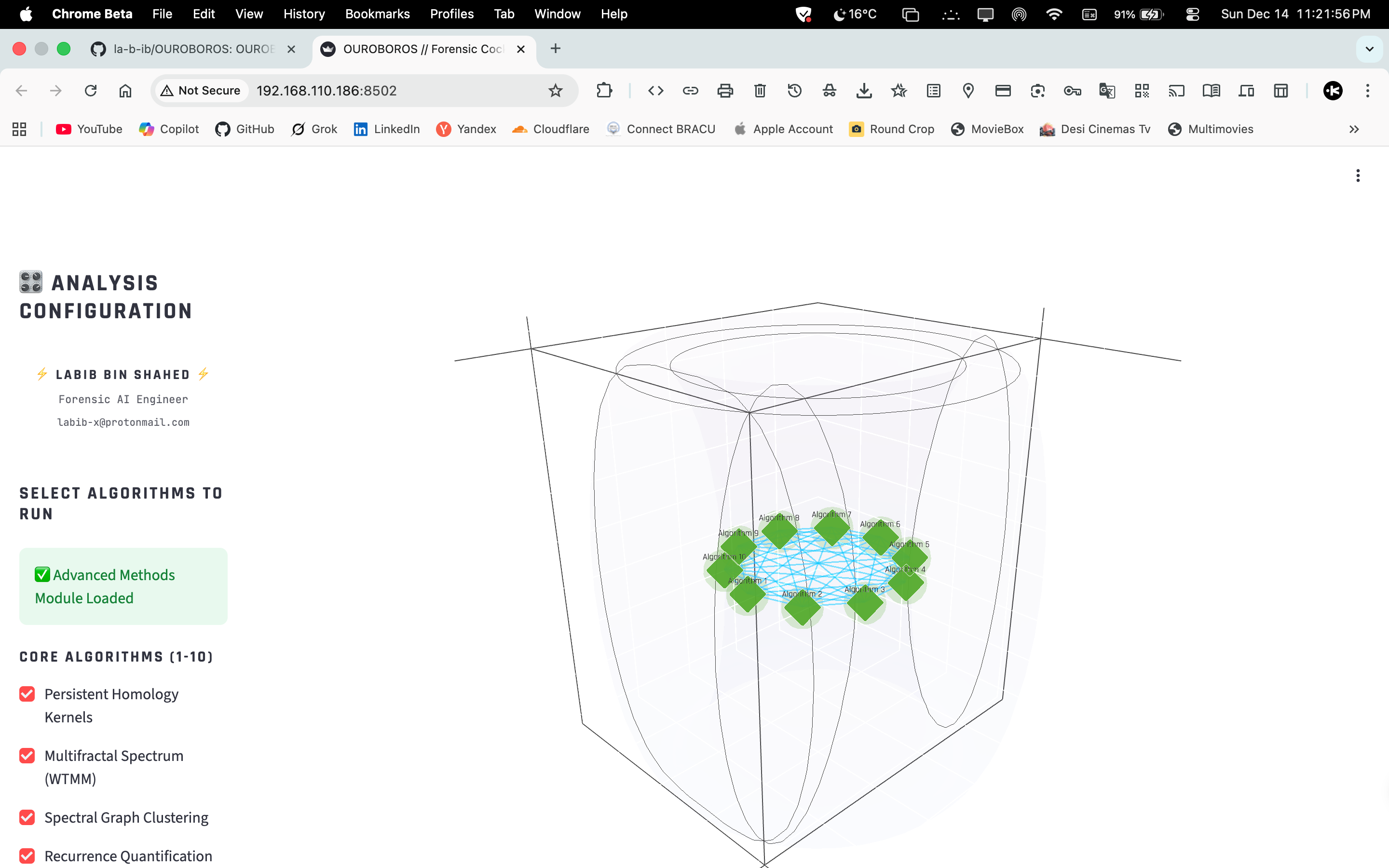
- Topology & Fractals — homology, zigzag, autoencoder, multifractal, fluid TDA.
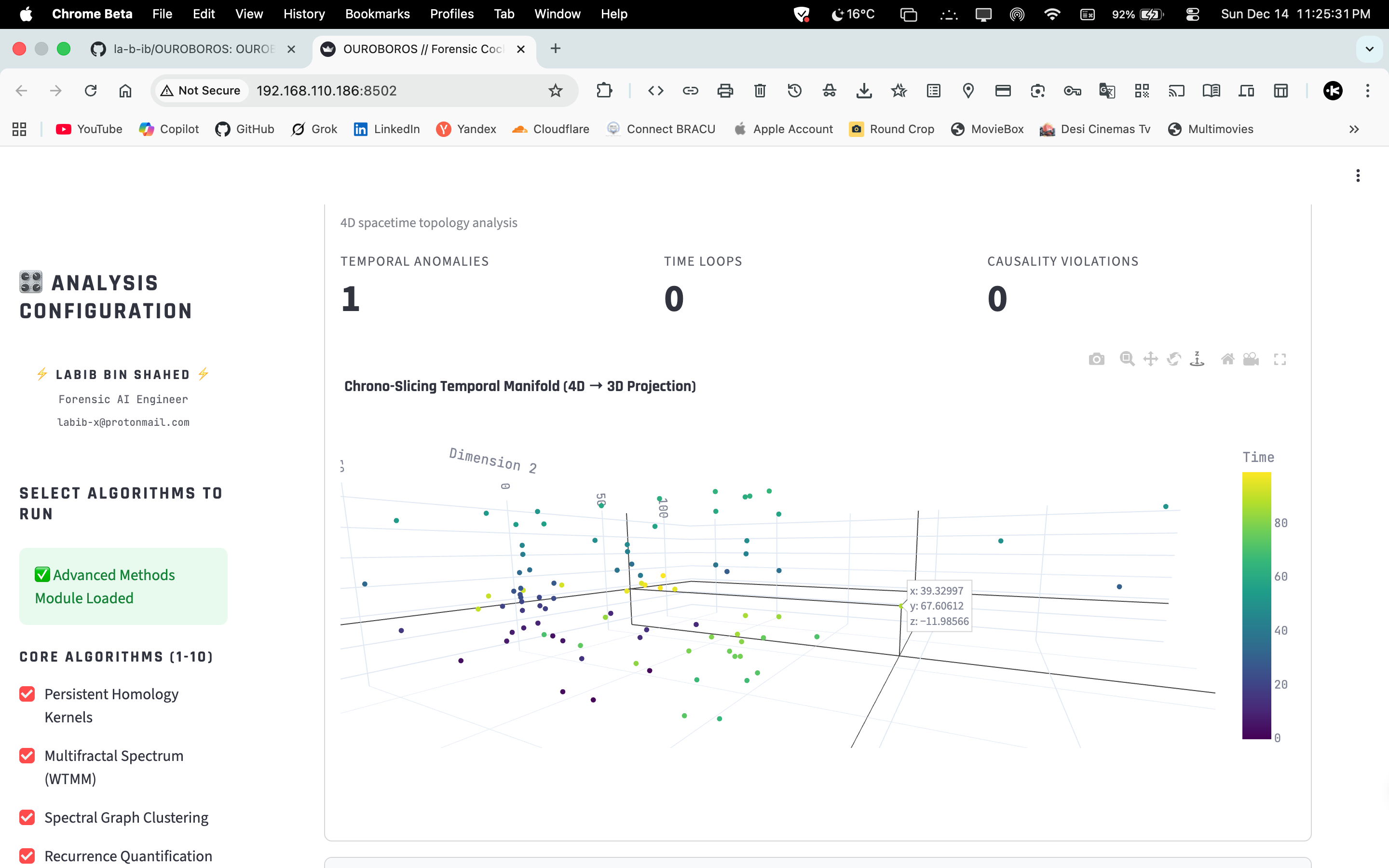
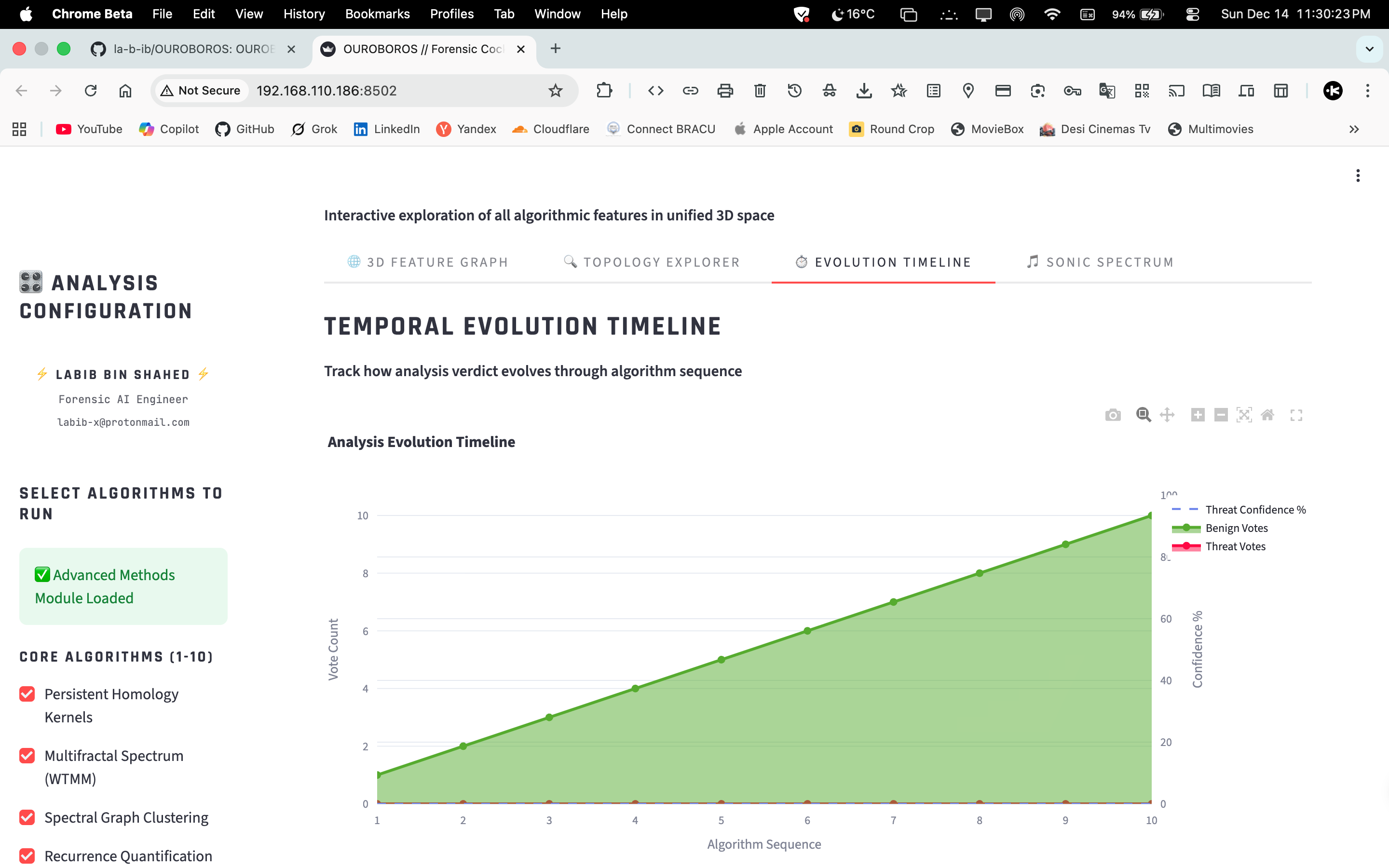
- Graphs & Dynamics — spectral clustering, DTW, quantum walk, symbiotic trees, chrono‑slicing.
- Entropy & Compression — NCD, event horizons, Benford, stylometry.
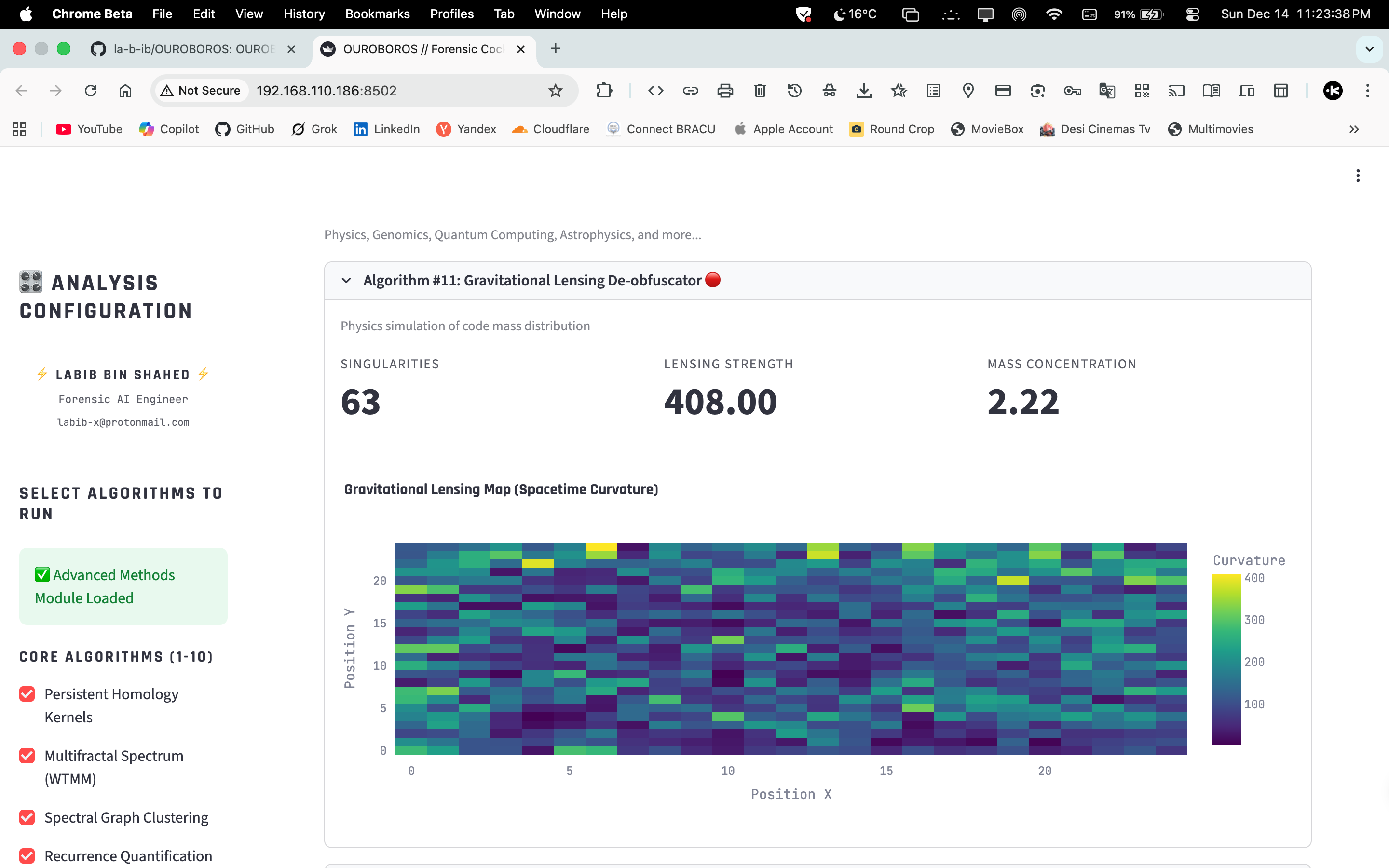
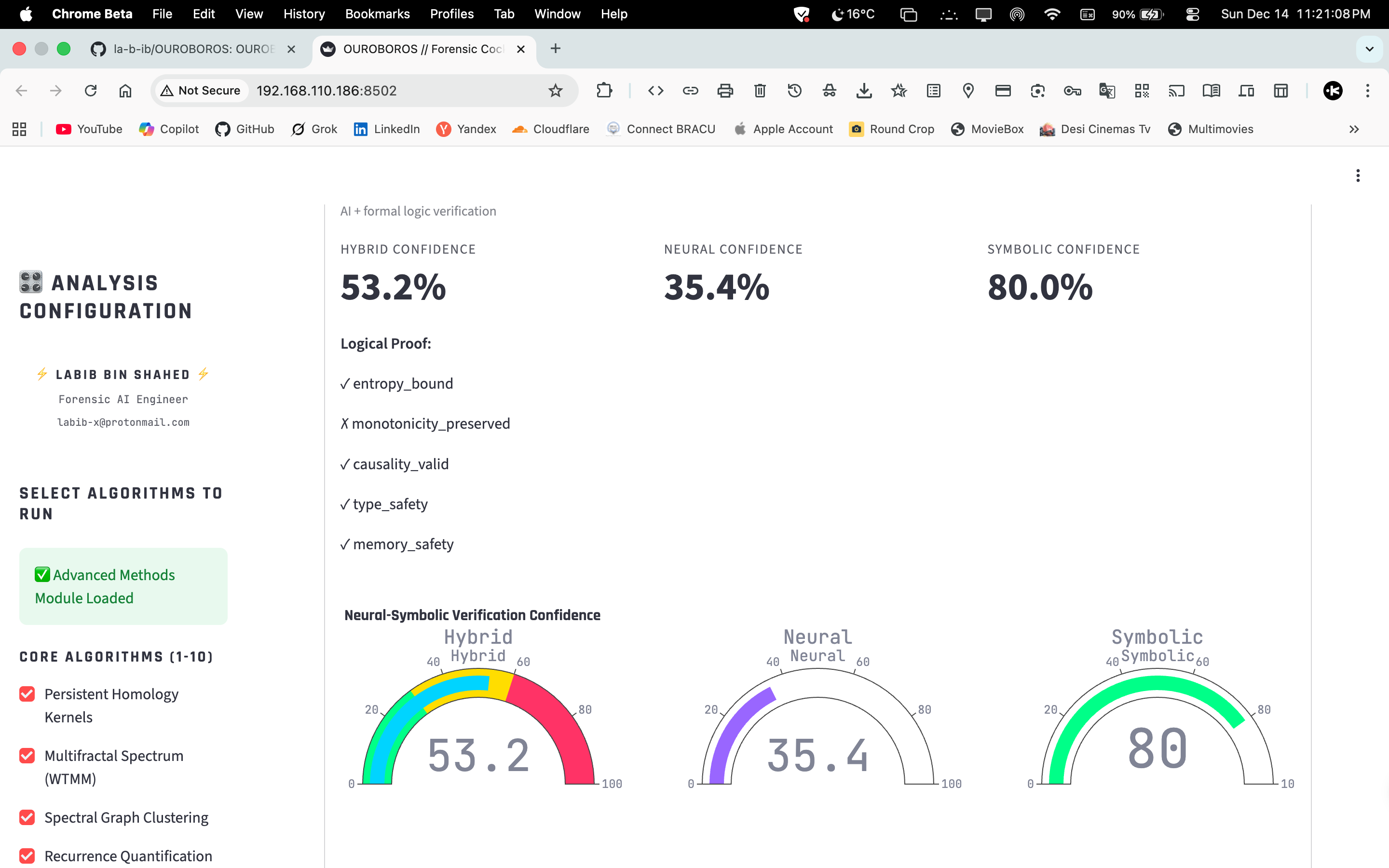
- Symbolic & Hybrid — Z3 execution, neural‑symbolic verifier, gravitational lensing.
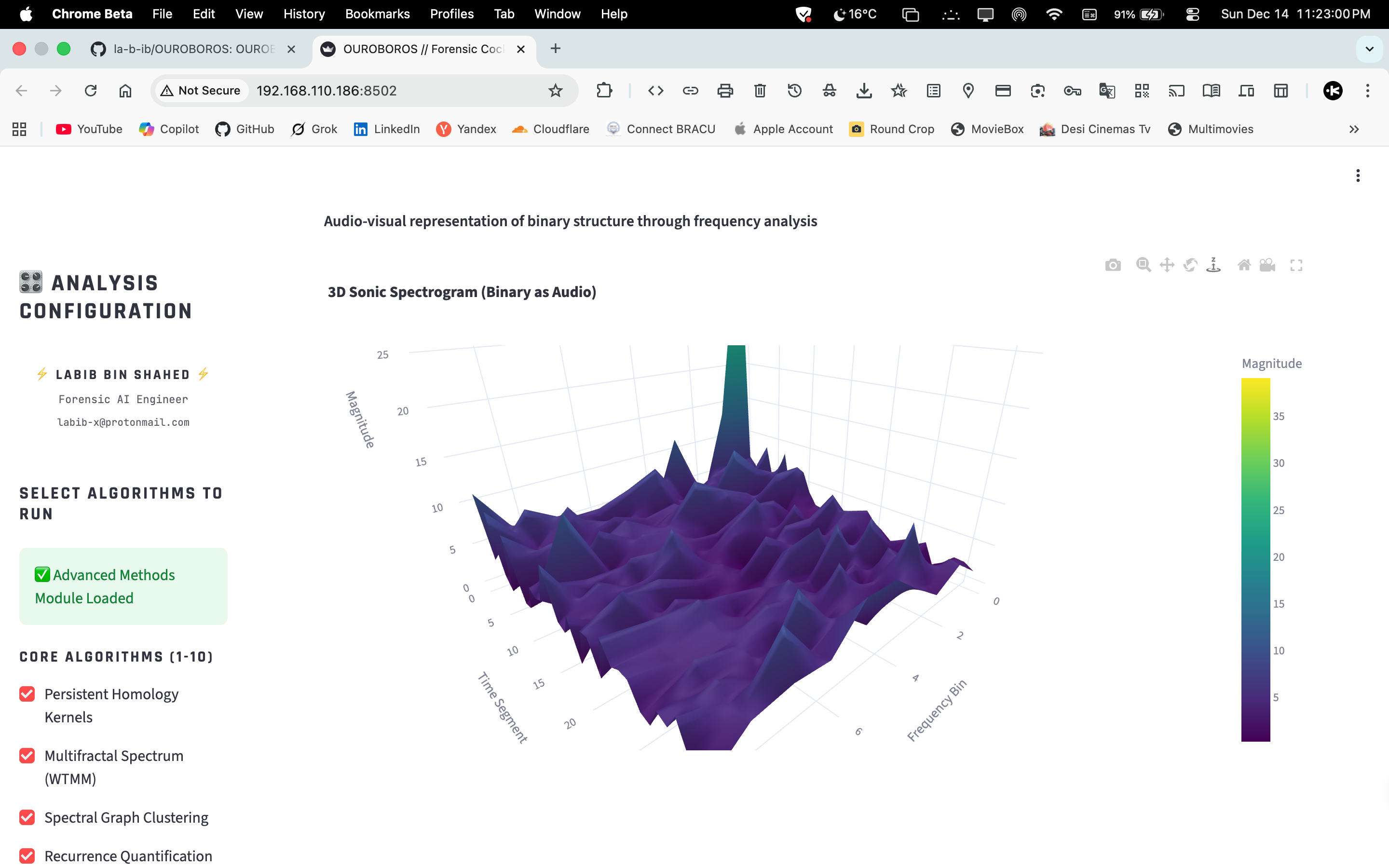
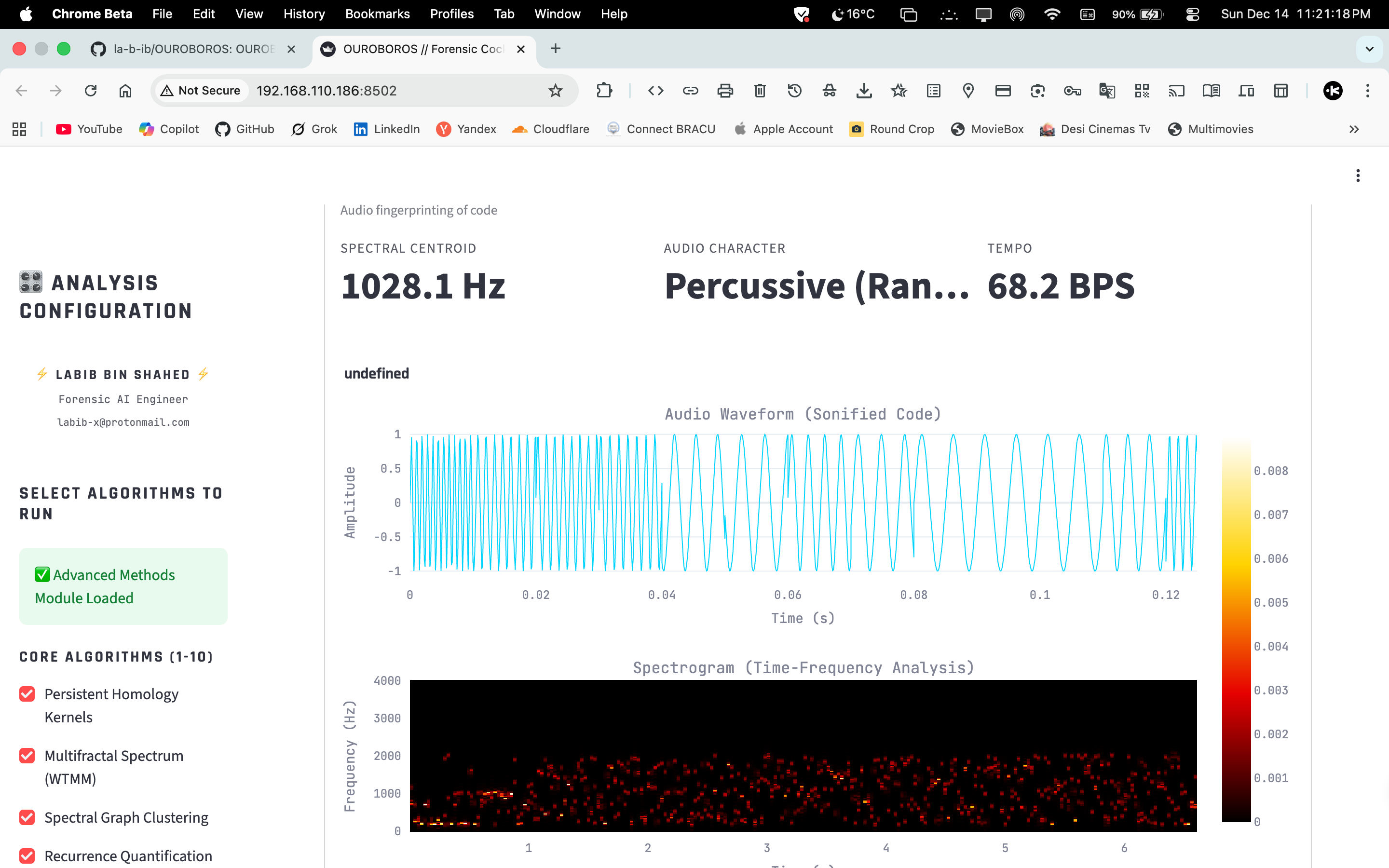
- Latent & Perceptual — LDA topics, MinHash LSH, RQA, sonification.
Mathematical Appendix
1. Takens' Embedding Theorem, VR Persistence Stability, Wasserstein Kernels & Persistent Entropy
For dynamical system
2. Multifractal Spectrum, RQA Quantifiers, Cheeger Inequality & DTW Optimization
Partition function:
3. NCD & Information Distance, Benford Distribution, MinHash Analysis & LDA Parameter Estimation
Based on Kolmogorov complexity
4. Lyapunov & Hurst Estimation, Isomap & LLE Optimization, QMC Error Analysis & Ensemble Fusion
Lyapunov exponent:
Architecture
flowchart LR
%% User Interaction Layer
USER["User"]
UPLOAD["Executable"]
SELECT["Algo"]
%% Core Processing
VALIDATE["Validation"]
EXTRACT["Extraction"]
%% Classical Analysis
TOPO["Topology"]
CHAOS["Chaos"]
BIO["Bio-Digita"]
SPECTRAL["Spectral"]
SYMBOLIC["Kolmogorov, MinHash"]
AUDIO["Audio"]
%% Threat Assessment
COLLECT["Collect"]
FUSION["Fusion"]
SCORE["Scoring"]
%% Results
METRICS["Metrics"]
VERDICT["Verdict"]
DETAILS["Details"]
%% Flow Connections
USER ==> UPLOAD ==> VALIDATE ==> EXTRACT
USER ==> SELECT ==> VALIDATE
EXTRACT ==> TOPO & CHAOS & BIO & SPECTRAL & SYMBOLIC & AUDIO
TOPO & CHAOS & BIO & SPECTRAL & SYMBOLIC & AUDIO ==> COLLECT
COLLECT ==> FUSION ==> SCORE
SCORE ==> METRICS ==> VERDICT ==> USER
SCORE ==> DETAILS ==> USER
%% Styling Classes with unified bold 25px text
classDef user fill:#e6f7ff,stroke:#004080,stroke-width:3px,color:#000,font-weight:bold,font-size:35px
classDef process fill:#fffbe6,stroke:#806000,stroke-width:2px,color:#000,font-weight:bold,font-size:35px
classDef classical fill:#d0e6ff,stroke:#004080,stroke-width:2px,color:#000,font-weight:bold,font-size:35px
classDef assessment fill:#ffe6e6,stroke:#800000,stroke-width:2px,color:#000,font-weight:bold,font-size:35px
classDef results fill:#e6ffe6,stroke:#004d00,stroke-width:2px,color:#000,font-weight:bold,font-size:35px
%% Assign Classes
class USER,UPLOAD,SELECT user
class VALIDATE,EXTRACT process
class TOPO,CHAOS,BIO,SPECTRAL,SYMBOLIC,AUDIO classical
class COLLECT,FUSION,SCORE assessment
class METRICS,VERDICT,DETAILS results
%% Bold connecting lines
linkStyle default stroke:#000,stroke-width:5px
References
The core references grounding this work span computational topology, dynamical systems, probabilistic modeling, and numerical methods. Foundational texts include Edelsbrunner and Harer’s Computational Topology and their stability results on persistence diagrams, Villani’s Optimal Transport for Wasserstein theory, and Strogatz’s Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos alongside Rosenstein, Wolf, and Ott’s algorithms for Lyapunov exponents. Bishop’s Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning provides background on LDA and probabilistic models, while Niederreiter’s work on Sobol sequences underpins quasi‑Monte Carlo sampling. Together, these sources supply the theoretical backbone for persistence, chaos analysis, probabilistic inference, and advanced sampling techniques.
Legal Disclaimer
OUROBOROS is provided solely for academic and research purposes. No warranties are expressed or implied, and the authors assume no liability for misuse, damages, or outcomes. Users are fully responsible for ensuring compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and ethical standards.