-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
Home
CACAO is a web platform developed according to the 12-Factor design pattern (for more information about '12-Factor' design, see https://12factor.net/). There are different parts of this application that run as autonomous internal services.
The following picture illustrates all of these internal components that are part of CACAO:
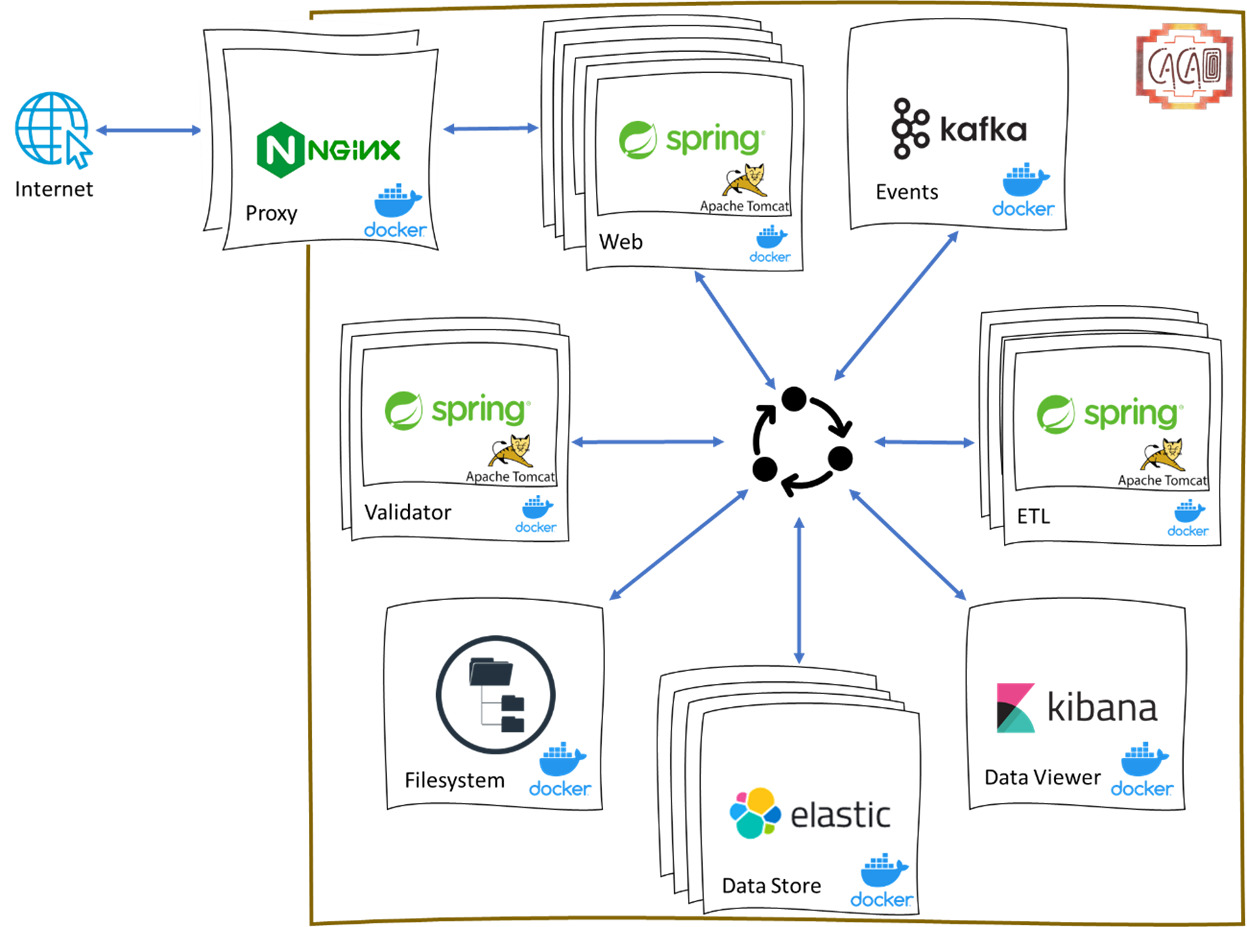
Each part of CACAO runs inside a Docker container, so it's possible to deploy the whole system in different platforms, including these options: cloud, on-premises, single-server, multiple servers.
It's possible to scale up any one of them by running multiple instances according to different needs. For example, if the 'validation phase' becomes a bottleneck in a scenario with high workload, it's possible to start multiple instances of the component related to 'validation'. On the other hand, to increase concurrency of multiple users, it may be necessary to start multiple instances of the component related to the frontend (the 'web' component). So, the overall system is flexible enough to accommodate different workload needs.
The following table summarizes information about these components that are part of the CACAO infrastructure, and how they relates to each other.
| Internal Component Name | Industry Technologies | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Proxy | NGINX, Let's Encrypt | This is the only component of CACAO infrastructure that will be directly exposed to the Internet. This component deals with the SSL certificate auto renewal process using certificates issued by Let's Encrypt Certificate Authority. NGINX is configured to be used as a 'reverse proxy'. It redirects all the incoming requests to the internal 'web' component. The other internal components are isolated and are not accessible from incoming requests. |
| Web | SPRING, JAVA, THYMELEAF | This is the main component of CACAO application. It's a Spring application written in Java and serves a web application (HTTP). It provides both a web user interface and a REST interface. The latter may be used directly for easier integration with other application servers. It makes use of "Spring Security" to strengthen many aspects of application-level security (e.g.: CSP, CSRF, RBAC, and others).The user authentication may occur in different ways: Basic credentials (login and password) OAuth2/OpenId (with external provider) Token for direct API use (for integration with external application servers) This component interacts with ElasticSearch, and Kibana using HTTP REST requests.This component interacts with Validator and ETL internal components using events streamed by KAFKA.It's also used as a proxy/gateway to Kibana user interface at some parts. |
| Validator | SPRING, JAVA | This component of CACAO is a microservice in charge of carrying out the validation procedure of the data contained in incoming file. A set of validation rules are configured at the application and applied at this phase. The outcome of this phase is a standardized general representation of the original records. This component interacts with ElasticSearch using HTTP REST requests.This component interacts with ETL internal component using events streamed by KAFKA. |
| ETL | SPRING, JAVA | This component of CACAO is a microservice in charge of carrying out the transformation of incoming parsed data to make available for use in dashboards and other built-in reports.This component interacts with ElasticSearch using HTTP REST requests.This component interacts with Web component using events streamed by KAFKA. |
| ES | ElasticSearch | This component represents the data storage for performing the analysis.It uses ElasticSearch configured as multiple nodes, holding multiple copies of data in multiple shards. The data replication ensures data loss protection and high availability. The nodes are synchronized internally using ElasticSearch features. |
| KIBANA | Kibana | This component represents the data visualization layer.It provides a toolkit for building and presenting dashboards over data published by the ETL internal component.This component interacts with ElasticSearch using HTTP REST requests.The Kibana web user interface is channeled through the CACAO 'web' component.Kibana's role based access control is kept in sync with the CACAO 'web' component's own control in order to keep a single sign-on. |
| KAFKA | Apache Kafka | This component is used to manage information traffic between all other internal components of CACAO and ensure that no messages are lost or duplicated. |
| ZOOKEEPER | Apache Zookeeper | This component is internally used by KAFKA. |
| Eureka | Apache Eureka | This component is used as a service registration and discovery. The purpose of this component in CACAO is just to keep a reference to all active services, in order to assist a system administrator. |
| Filesystem | * | The CACAO file storage may reside in different locations as per the internal configuration provided by the system administrator.The basic deployment configuration makes use of the local file system on the host machine. In cluster or cloud deployment, it's possible to adopt a distributed or remote file system. |
These are the development standards that were defined for this project:
1 – Java code documentation: Every Java class must contain documentation conforming to the JavaDoc standard, in English.
2 – Charset: The charset must be UTF-8 for all the following files: Java, HTML, CSS, JS and text files in general.
3 – API documentation: Every controller method that exposes some REST functionality to be used by an external audience must adopt SWAGGER annotations (e.g.: @ApiOperation).
4 – Naming convention: Every name used for a class, method or field must follow the CamelCase pattern (method starting with a lowercase letter, class with a capital letter), using words in English, preferably short names. Underscores should be avoided, except for naming fields in ElasticSearch mappings or for integration to external resources.
5 – Internationalization : Every text message displayed to the user cannot be hardcoded. It must be inserted in 'message.properties' file of web module and only their key names referenced in code. The same applies to HTML content. Dates, times, months and numbers must be formatted according to the regional conventions. Additional 'message.properties' files may be considered for different languages support. We have translations for all these messages in at least two languages: English and Spanish.
6 – Directory structure : Adopt the MAVEN directory pattern (i.e.: "/src/main/java" for source code related to the application, "/src/main/resources/" for miscellaneous resource files used by the application, "/src/test/java" for source code related to test cases, etc.). All HTML contents used as 'template' for generating dynamic pages must be included inside the directory "/src/main/resources/templates". Every fragment of HTML content that is reused in different HTML pages must be included in the directory "/src/main/resources/templates/fragments". All static content of type JS, CSS, HTML and images must be included inside the directory "/src/main/resources/static".
7 – Java package convention : All the internal Java packages must be organized according to these standards:
- All persistent entities must be defined inside the 'entities' package.
- All repository classes must be defined inside the 'repositories' package.
- All error/exception class definitions must be defined inside the 'errors' package.
- All utility classes must be defined inside the 'utils' package.
- All controller classes exposing user interface must be defined inside the 'controllers/ui' package.
- All controller classes exposing REST interface must be defined inside the 'controllers/rest' package.
- All service classes for internal use of the module must be defined in the 'controllers/services' package.
- All MVC transfer objects from controller to view and vice-versa must be defined inside the 'dto' package.
- All classes used exclusively for the purpose of configuration must be defined in the 'config' package.
- All specific code related to security (e.g.: web-filters related to authentication) must be defined in the 'sec' package.
- All aspect-oriented code (i.e.: pointcuts and advices) must be defined in the 'aspects' package.
8 – Dependencies : All dependencies to third party JAR must be entered in the POM file according to the MAVEN standard. All dependencies must comply to a permissive or weakly protective license, such as: Apache, BSD, MIT, LGPL.
9 – Test unit cases : There must be a test case according to JUnit standard for every functionality or set of functionalities.
10 – Application properties : Parameters that change the application behavior but are not changed directly often should be defined in the 'application.properties' file instead of being hardcoded. On the other hand, if the parameter is supposed to be changed frequently, it must not be defined statically, but be dynamically provided through user interface.
11 – Singletons : Every 'singleton' must be implemented in the form of a "Bean" conforming to the Bean pattern according to the Spring framework.
12 – Dependency injection : The internal dependencies between different classes related to services, controllers, components or 'Java Beans' in general must be performed using Spring injection strategies (often with the use of the @AutoWired annotation).
13 – Logging : Use 'java logging' pattern for registering log events inside the code with the appropriate log level for each situation. Should not use 'System.out.print', 'System.err.print', 'printStackTrace' or anything like that.
14 – Static content provisioning : Static content such as JS and CSS found in public frameworks (e.g.: JQuery, Tabulator, etc.) must be embedded in the project and not be directly referenced from public repositories. Use the 'minimalist' version whenever possible.
15 – Javascript contents in HTML pages : Every <script> tag present in HTML pages must be kept by the end of the file and must make use of the 'cspNonce' parameter, as shown in the example:
<script th:nonce="${cspNonce}" th:inline="javascript">
16 – Spring Security Annotations : Every method exposing contents through user interface or REST request should be annotated with the @Secured annotation and provide specific 'roles'. The set of all roles is enumerated in the 'SystemPrivilege' class.
17 – SQL Injection : Never ever concatenate input parameters with SQL contents. Every operation related to persistence must make use of parameterized alternatives in order to avoid SQL injection attacks.
18 – Text input : All text-type input parameters that can be supplied by the external user must be handled before being stored in database. For example: truncating long sequence of characters if they are too big, escaping HTML-like contents, removing non-printable characters, etc.
19 – Reactive user interface : Every user interface should be well-presented on both large desktop screens and small cell phone screens.
20 – CRUD and queries : The user interfaces related to CRUD operations (create/update/delete) and queries must conform to a set of patterns. Query results must be paginated and include filtering capabilities.
21 – Source code quality : All the source code must comply to the SonarQube standard settings and be reported with the following results:
- Less than 3% of duplicated lines on code.
- Maintainability minimum rating: A.
- Reliability minimum rating: B.
- No bugs under the following categories: Blockers, Critical, Major.
- Security minimum rating: B.
22 – Index naming for storing data : Every index stored in ElasticSearch related to CACAO objects must be prefixed with '_cacao\ __'. Data produced by the 'validator' phase must be prefixed with 'cacao_doc_'. Data produced by the 'ETL' phase must be prefixed with 'cacao_pub_'.
23 – Endpoint URL naming convention : Every endpoint related to REST API must start with '/api'. Every endpoint must use hyphen for separating words, as in the following example: /api/analysis/vertical-horizontal-analysis .
24 – License notes : Every Java class must include the licensing information (according to the BID license) at the beginning of the file.
The complete source code of CACAO may be found in a GIT repository:
https://github.com/EL-BID/CACAO
The branch ' master' contains the last version of the code.
The software developed in CACAO project is licensed accordingly to the MIT license. A copy of the license may be found in the 'LICENSE.txt' file in the root of the project, including reference to the licenses of third-party components.
The 'README.md' file and other 'README*.md' in the root of the project includes several information related to:
- Installation procedure for developer environment.
- Installation procedure for production environment.
- Additional information for cloud environment.
The root of the project also includes additional files related to Docker Compose for easy deployment on different platforms. The subdirectory 'conf' contains additional configuration files used for deployment.
The subdirectories are mostly related to 'modules', as described in the next chapter.
CACAO was developed with focus on modularization for increased maintainability. There are several ' modules' for different purposes as described in this chapter.
Some parts of CACAO were developed as a ' plugin' in order to separate from the general purpose architecture all domain specific features, such as definitions of 'accounting data'. In the future, additional domain-specific features may be developed and introduced as additional plugins in additional modules (for example, there may be a new plugin related to 'electronic invoces'). All CACAO plugins must conform to Java Service Provider Interface (SPI) and must implement the interface 'TemplateArchetype' defined in 'api' module.
| Module Name | Module Description |
|---|---|
| proxy | This module serves the docker definition for the 'PROXY' component of CACAO infrastructure. The main piece of this module is the 'Dockerfile' file. The internal 'config' subdirectory contains additional configuration settings related to NGINX. There are no source codes defined here. |
| api | This module contains Java code shared between different modules ('web', 'validator' and 'etl'). The resulting JAR is incorporated as a 'direct dependency' in each of the other dependent modules and is considered 'required' at runtime.It defines the common elements for the entire system, such as the 'document template' definition and all its internal field mappings.It also implements some utility methods that are commonly used. |
| mock_es | This module is only used for testing each module individually according to unit test cases.This module contains Java code for a utility object that 'mocks' an ElasticSearch server with only a few features implemented.Other modules may use this artifact for performing test unit cases without the need of a 'real' Elastic Search deployment.It's not used in runtime. |
| account | This module contains Java code related to the CACAO Accounting Plug-in.It contains archetype definitions related to account data, such as: Journal, Chart of Accounts, Opening Balances, etc.The validation rules and ETL transformations that are specific to accounting data are also implemented here.The resulting JAR is incorporated to the other modules as an optional dependency and is required for dealing with accounting data. |
| eureka | This module contains Java code for implementing a simple 'Eureka Discovery Server'.There are also additional Docker files for provisioning this application as a container. |
| web | This module contains Java code related to the 'WEB' component. It's a SpringBoot web application with both user interface and REST interface. There are also additional Docker files for provisioning this application as a container. |
| validator | This module contains Java code related to the 'VALIDATOR' component. It's a SpringBoot application with a REST interface, but its core functionality is provided by SpringCloud streaming connections (i.e. using KAFKA). There are also additional Docker files for provisioning this application as a container. |
| etl | This module contains Java code related to the 'ETL' component. It's a SpringBoot application with a REST interface, but its core functionality is provided by SpringCloud streaming connections (i.e. using KAFKA).There are also additional Docker files for provisioning this application as a container. |
| kibana | This module serves the docker definition for the 'Kibana' component of CACAO infrastructure. The main piece of this module is the 'Dockerfile' file. There are additional configuration files related to Kibana.There are no source codes defined here. |
| es | This module serves the docker definition for the 'ElasticSearch' component of CACAO infrastructure. The main piece of this module is the 'Dockerfile' file. There are additional configuration files related to ElasticSearch.There are no source codes defined here. |
| tests | This module is only used for integration tests.This module contains Java code for performing the integration tests with all the CACAO modules.It makes use of 'test-containers' framework for initiating each component for testing purposes.It does not use 'mock-es'. An actual ElasticSearch deployment is used instead.It's not used in runtime. |